How to judge morality and its impact on human life?
The Moral Dilemma
A healthy sense of good and bad makes a society livable. There are some special, rare events that happen in the society we live which challenge our idea of what is good and what is bad. There are uncountable offenses and also in varying types which create problem of who should actually be punished and what should be the punishment.
An eye for an eye will make the whole world blind.
Mahatma Gandhi
If this is really the case, the law and order should punish the victim in such a way that it prohibits the future perpetrators to not do such crimes again. But again, as this above mentioned quote goes if the punishment given for the crime is equally dangerous then what exactly are we trying to establish through such punishment?
It’s like that scenario where murdering a murderer creates a new murderer so the net number of murderers in the society remain the same. An Italian philosopher called Cesare Bonesana di Beccaria had given a thought on this. In his book ‘Of Crimes and Punishments’ he discusses that if the punishments grow on crueler and crueler the net mindset of people also grows crueler. It’s like how water levels itself irrespective of the depths. The baseline of what is right and wrong furthermore what is more wrong and what is more right shifts up. Crueler and crueler crimes reduce the sensibility of people of that society. This could be one reason why people always argue that the judicial system does not provide equivalent punishment as a justice to the victims of certain heinous, exceptional cases of crimes. (Although there are many other factors to make such decisions.)
“In proportion as punishments become crueler, the minds of men, as a fluid rises to the same height with that which surrounds it, grow hardened and insensible; and the force of the passions still continuing, in the space of a hundred years the wheel terrifies no more than formerly the prison. That a punishment may produce the effect required, it is sufficient that the evil it occasions should exceed the good expected from the crime, including in the calculation the certainty of the punishment, and the privation of the expected advantage. All severity beyond this is superfluous, and therefore tyrannical.”
Cesare Beccaria, Of the Mildness of Punishments from ‘Of Crimes and Punishments’
In similar spirit, the relationship between Batman and Joker can be understood. Joker never cares about killing people he will try to stretch the limits of batman in every possible sense where innocent lives are at stake. Batman has one solution to stop all this – to kill the Joker. But with a high moral ground Batman would never kill Joker. What is the motivation behind such character design of Batman. Batman knows that killing Joker would solve the problem once for all. Believe me, this is not just a fictional comic book scenario. The reality that we live in has uncountable such scenarios where exactly same decision dilemmas occur.
The famous trolley problem also points to somewhat similar moral dilemma. Where should the trolley be directed if one track has single person and another has 5 people tied to the track? Nobody wants blood on their hands.

But the same trolley problem becomes interesting if you start adding additional attributes to the people who are on track.
What if the single person tied to the track is a scientist with the cure for cancer and the track with five people are criminals? Then definitely you would kill the five criminals instead of the single scientist.
Did you notice what change made us to decide faster? The moment we understood the consequences of our actions we had the clarity of what is right and what is wrong. Our moral compass pointed to North the moment we foresaw the consequences of our actions.
The foundation of some of the principles of morality are based on similar ideas. Utilitarianism and Jeremy Bentham’s an English Philosophers ideas have contributed to the ideas of morality for humanity, especially when we are talking about the human society as a whole. The ideas put by Jeremy Bentham also faced severe criticism, we will see those in detail too. But the key intention of my exploration is to understand how we create the meaning of Morality and how subjectivity, objectivity totally change the way we perceive morality. In the end we may reach to rock bottom questioning the morality itself to be nonexistent – and if morality is non-existent then what separates human beings from animals? (I hope to enter in this territory with some optimism, I don’t know where will it end.)
Utilitarianism
As I already explained in the trolley problem that by adding one simple, short part of information shifted our moral compass in (supposedly) proper direction. What did this information add in the dilemma to make it solvable?
The answer is the foresight of consequence. Once you saw the consequence it leads to you got the hold of what is right and what is wrong. You decided one side to be right and other one to be wrong. This foresight of consequence helped you to weigh the ‘right’-ness of your decision.
Utilitarianism is based on the measurement of morals based on the consequences of the actions you take. What is the other side of taking actions? It is ‘the intent’. This is where the fun game begins.
Many philosophers are always fighting over morals based on the intent of the person and the consequences of the actions they take. For example, thinking of murder (pardon my thinking) makes me less of convict than really murdering someone. My thinking has not led to the loss of the person I hate. Utilitarianism thus calls out for the construct of morality based on the actual actions and their consequences; it’s like saying ‘what a man is more about what he does instead of what he thinks’.
Hedonism, Utilitarianism and Jeremy Bentham

Happiness is a very pretty thing to feel, but very dry to talk about.
Jeremy Bentham
Jeremy Bentham an English philosopher contributed to the utilitarian ideas of morality. He was not well appreciated in his home country due to the misalignment of his ideas of socio-political reforms with the British sovereignty of those times. The French translation of his works on law, governance gave him popularity in Frenchmen. Bentham was one of the people who pushed the political reforms during French revolution.
While reading Joseph Priestly’s Essay on the First Principles of Government, Bentham came across the idea of “greatest happiness for the greatest number” which motivated him to expand the ideas of utilitarianism.
Priestly brought the idea of “Laissez-faire” (‘allow to do’ in French)- a policy of minimum governmental interference in the economic affairs of individuals and society. Joseph Priestly developed his ideas of politics, economics and government based on the ideas created by Adam Smith (Author of the Wealth of Nations – the holy grail of classical Economics).
The Greek philosopher called Epicurus was the supporter, creator of hedonism. Hedonism defines ethics to pleasure or pain. According to hedonism that which gives pleasure is morally good and that which give pain is morally wrong. The idea behind hedonism is the aversion of pain to live an undisturbed life because anyways this all won’t make sense once you are dead. According to Epicurus – fear of death, retribution is pushing people to collect more wealth, more power thereby causing more painful life. The collection of wealth, power is done thinking that they can avert the death but that is not the reality. So, worrying about the death sucks out the pleasure of living the life which itself is equivalent of death.
Non fui, fui, non-sum, non-curo
Epicurus
(“I was not; I was; I am not; I do not care”)

So, epicurean hedonistic morality tries to maximize the pleasure. The other end of this idea is that if everyone tries to maximize their own pleasure (egoistic hedonism) wouldn’t it disturb others?
If I want to listen to a song on loud speaker while bothering my neighbors, what is the moral standpoint here?
The answer is the overall good of the system. So, if you neighbor also wants to listen music loud and overall loud music is good for the group then we are morally right to play loud music. (Just pray that the group has same music interests!)
So, Jeremy Bentham is known to rejuvenate this ancient philosophy of egoistic hedonism through his philosophy of utilitarianism.
The basic idea behind Utilitarianism is to maximize the utility of anything, value of anything. The utility can be increased by doing what is right which can be done by doing what gives more pleasure or by avoiding those things which increase or give pain.
Utility is a property which tends
- To produce benefit, advantage, pleasure, good or happiness
- To prevent happening of mischief, pain, evil or happiness
So, the right action is the one that produces and/ or maximizes overall happiness. Please understand that the word “overall” is important for Jeremy Bentham’s philosophy of Utilitarianism. Because from selfish point of views, what is pleasurable for one may not be pleasurable for others. (This is also where the certain philosophical problems of Utilitarianism are hiding, save this point for later.)
To solve this bottleneck of clarity, there are two types of pleasure in human life – one is happiness from senses, physical experiences and one is from intellect. The intellectual happiness is higher than the pleasure from senses. So, on personal moral dilemmas these two attributes can solve the problem.
All good on personal level but what about the moral decisions for the group, for society? Here, Bentham solved the moral dilemma by using the idea of “greater good for all”. When we don’t agree on what makes us happy together, making sacrifices in your happiness to make others happy is the solution. (Keep this idea parked in your mind.)
“Nature has placed mankind under the governance of two sovereign masters – pain and pleasure. They govern us in all we do, all we say and all we think.”
Jeremy Bentham
Felicific Calculus – Measuring happiness
Jeremy Bentham is known as the Issac Newton of the Morality for developing the felicific calculus/ hedonistic calculus. Bentham pointed out the key factors which affect the net happiness and using this factors’ effect as a whole, one can quantify the happiness.
Following are the factors which affect the happiness:
- Intensity – how strong is the pleasure from the given action?
- Duration – how long does the happiness remain from given action?
- Certainty – what is the likelihood of given pleasure to occur?
- Propinquity – how soon/ immediate is the occurrence of the pleasure?
- Fecundity – what is the possibility that this pleasure will also lead to the newer pleasure(s)?
- Purity – what is the change that this pleasure will not bring some opposite sensation?
- Extent – how many people are affected?
If one considers these factors and the principle to maximize the communal happiness, most of the social moral dilemmas can be effectively solved.
So, according to this felicific calculus,
- Batman should kill the Joker for the greater good of the Gotham
- The trolley should go over the group/ person which creates more pain for the society
- Baby Hitler should be killed once we get the chance to travel back in time
You must appreciate the clarity which the felicific calculus brings. This clarity is very important for the policymakers, politicians while deciding the fate of the group, state, nation as a whole.
Now a simple question –
If batman keeps on killing the villains, won’t he become the greatest killer of them all? What would differentiate Batman from other villains?
What would happen if you were given false information about the nature of the people tied on track while riding that trolley? Could your wrong decision be undone? If it was the wrong decision then now ‘you’ are morally wrong, with the blood of the innocents.
You would kill baby Hitler only because you have vision that this baby will grow up to be the mass murderer tyrant. The mass murder hasn’t happened yet. So, now you are the killer of a ‘now’ innocent baby.
Maintaining same emotion, now you would appreciate why even for a strong judicial system giving capital punishment for rapists, terrorists is difficult morally. You would solve the problem for now because the act has been already done, the consequences have already happened (which is why moral judgement is effective as it relies on the consequences). Killing the perpetrators or punishing them with equal pain would definitely bring peace of mind using the principles of morality but that also degrades the morality of innocents who fell down from that morality. It is not matter of what one deserves because what bad happened to them, it is about how less human you will become once you perform that act of punishment.
Recall the quote of Beccaria in the early part of my discussion.
Killing joker will create fear among other villains but it also creates chance for the creation of even dangerous villain in future.
Killing baby Hitler doesn’t guarantee prevention of World War and mass murders, as our personalities are the result of our surroundings – another Hitler-like person would have emerged in such given circumstances. (I honestly don’t know if he/she would be worse or less harsh than the original one but you get the point – conditions anyways would have created another cruel person.)
Jumping out of the trolley seems the best way to run away from the pain of murder of other unknown people (joking). The trolley dilemma remains dilemma.
Also, the felicific calculus allows pain for small groups for the betterment/ pleasure of the bigger society. For example, according to this utilitarian idea killing few healthy convicted prisoners to save lives of many innocent people by harvesting the prisoners’ organ is justified. It is for the good in the end.
You see where this goes?
See the level to which any human or a group could go if they start justifying their moral rightness using these ideas. Using these principles any big group can overpower the minorities in morally right way. It is just a matter of time that the felicific calculus principles would get exploited for other “immoral” gains.
That is exactly why many people criticized the felicific calculus saying that a pig laying in the mud for his whole life would be happiest than a human being (Socrates to be specific) if Bentham’s calculus is used to decide morality.
In a crude way, there are two type of Utilitarianism which help to solve the problem to certain extent, but it is not a complete solution:
- Act Utilitarianism – to act for the greater good of all
- Rule Utilitarianism – to set rules in such way that no one inherently gets the pain or everyone is happy because actions and their consequences are bound by certain set rules in first place now
Happiness is not the ‘only’ and the ultimate goal – the limitations of Jeremy Bentham’s Utilitarian Philosophy
What people were not ‘happy’ with Jeremy Bentham’s felicific calculus was that it made humans more like machines and very objective. People don’t always want happiness for their or the group’s greater good. Exercising daily, reducing fat-sugar maybe painful but that guarantees healthy, illness free long life. Doing drugs isolates the person from pain but it impacts the long-term physical and mental health of the person. Hardships and pain make people to reach their difficult goals which is what is the real and ultimate happiness for them.
Happiness is not always the goal of life, if one is completely tangled in the pleasures of life and if everyone is having same mentality then in the end no one will be happy, because as a group we all would never agree on what makes us happy; different environments in which we grew, our personal experiences, our upbringing, our motivations prevent us from creating a common definition of happiness.
The subjective factor of pleasure or pain is not present in Bentham’s philosophy of Utilitarianism. Building further upon that, the victim who has suffered from the morally wrong action will only be satisfied when he/she gets justice, not when they are made happier than their perpetrators. (This justice must again not be mechanical and objective like the felicific calculus.)
One more flaw of the Bentham’s utilitarianism is the imbalance between personal scenarios and the communal scenarios. In most cases, it demands personal sacrifice irrespective of their subjective morality for the betterment of the group. (that is exactly how many past cruel dictators have justified their moral correctness on their acts against the minorities.)

A British philosopher, Bernard Williams presented a thought experiment to highlight such flaw of the Utilitarianism.
In this thought experiment:
A botanist on his South American expedition is ordered by the cruel regime soldiers to kill one of the Indian tribe people. If the botanist fails to kill one Indian the soldiers would execute all of the tribe members.
So, if we implement utilitarian principles, then the botanist should kill one Indian to save the remaining all. That is morally right.
But on the other hand, one must also understand that the botanist has nothing to do with the cruel regime and even with the indigenous tribe members. He is under no moral obligation to do anything. The consequences are in such a way that whatever he will do he will be called morally wrong. Which in the end is wrong.
The utilitarian philosophy neglects this subjectivity and consequentialism while we are deciding morality of anything.
Maybe that is also why even when we have all the rules in place, penal code in place for all types of offenses, similar crimes – we have a judge – a subjective, consequential observer to grant the final justice.
You must understand that the discussion does not want to pose Utilitarianism as completely wrong idea. The intent of this discussion is to understand how to de-clutter a complex moral scenario and how to inject subjectivity in it so that the correct person will get the justice in the end. As we are human beings and not machines, every day brings new subjective scenarios with new subjective moral dilemmas. Direct implementation of utilitarianism may bring in the transparency in the moral puzzle but it is at the expense of oversimplification and loss of personal subjectivity, consequential personal point of view and also freedom of person to exist.
The ways in which Utilitarianism brings immediate clarity by elimination of some important subjective aspects is dangerous and limits the judgement of real morality. Friedrich Nietzsche had warned new philosophers in his book beyond good and evil about the philosophies which create such “immediate certainties” like Utilitarian philosophy creates-
“The belief in “immediate certainties” is a moral naivete which does honor to us philosophers; but – we have now to cease being “merely moral” men!”
Friedrich Nietzsche
Conclusion – If not happiness then what is the goal of being human?
Jeremy Bentham’s philosophy of Utilitarianism and the felicific calculus can help to decide the morality of what is good for all but it ignores the presence and worth of personal integrity, the well being of the minorities, subjectivity of the person in given consequences. It by default eliminates the possibility of humans remaining human beings instead it attributes them as the machine maximizing a targeted outcome (which is pleasure here).
So, the question remains – If we are not meant to maximize pleasure during our tenure in life because in the end after death there will not be anything to experience or gain happiness – if our existence and final purpose does not align with being happy then what exactly is the purpose of being a human being?
Based on my understanding on what many great people have commented about the purpose of life, I found that most of them point to remaining the human being you always were. I am not saying that the personality should remain the same, rather it should change and keep on upgrading itself till the end but the core should remain same or it should not degrade at least.
Some wrong events, injustice, oppression, cruelty will make you suffer, but that should also not vilify your human spirit. Once we let go the pursuit of happiness and chase the goal of being a better human being (or at least remain the human being you are) we can fulfill the purpose of our lives and also make other people’s lives better.
Once you will let go of such utilitarian, mechanistic setups of morality you will realize that people don’t need gods, religions, governments, judicial systems to keep in the check of right and wrong. Our inner compass is more than enough to take care of what makes us human beings, this inner compass is not about what is right and wrong, for me it is about what better version of yourself you would become if you act in that certain way. It takes care of what you are thinking and what would be the consequences of actions thereby resolving the dilemma of morality which got separated on the basis of either intent or the consequences.
I am highlighting the importance of inner personal human compass because the rules designed to keep morality in check would always need revision and the utilitarian philosophy would wait for the consequences to happen to decide the morality. The goal of human struggle to improve their current version to a better one does not need either of the metrics to decide the morality.
Imagine what the world would become if everyone started appreciating this inner human compass!
(For now, we can only imagine, but I am optimistic on this.)

P.S. –
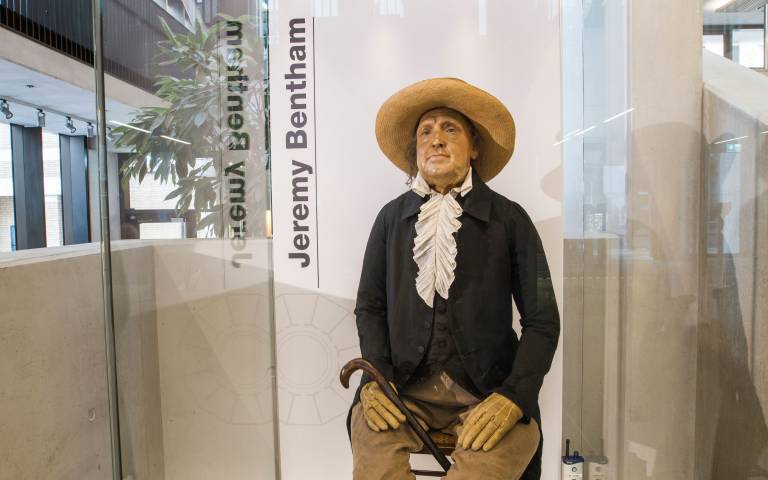
Even though the Utilitarian philosophy had many flaws, Jeremy Bentham contributed largely to bring in new political reforms, improve governance, establish penal codes in judicial systems, define sovereignty, reduce the influence of religious institutions on the lives of people and governments. His works were strategically maligned by some lobbies to lessen the impact of his other notable works. He was the proponent of liberty and freedom from religious influences on lives of people. The pushed for the establishment of a secular educational institute in London – now famously known as University College London. Jeremy Betham’s fully clothed wax statue containing his original skeleton remains in the entrance hall of the University main building upon his request.