Jacques Derrida’s philosophy for the better understanding of the reality

Language and its purpose
Questioning is at the core of philosophy. Philosophy’s main pursuit is always to create an understanding about the subject of interest. It provides a way to create a basic and concrete understanding of the subject. It is a way to understand the creation and things that are beyond creation. Philosophy is the process of formalizing any concrete understanding so that a new evolved, more absolute understanding could be built upon that foundation.
The means to create such understandings are languages; it could be any language, of symbols, pictures, sounds, geometries, etc. Language serves as the most important tool to formalize any thought, idea, proof, postulate. So, every component of the language has to mean something to create a bigger meaning; like in speech, every word means something. When I say ‘child’ you will see a human young-ling, when I say ‘apple’ you see a red fruit of that particular shape, and when I am saying apple, you are sure that I am not talking about ‘oranges’, because orange is associated with something different looking ‘fruit’ (some would even think of an iphone when I say apple!). This shows that just like how atoms create molecules thereby the object, in similar sense, words of basic meaning create an expression and thereby some context which shows what we mean when we are saying them together to convey a bigger meaning.
Just like atoms of different elements from the periodic table come together in different permutations and combinations to create variety of compounds and infinite objects rather the whole universe, in the same sense every component of given language carries a value – a meaning which builds a narrative, an expression to create a context, a logical statement; a set of such logical statements together can point to some truth, some fact. If used in smart ways, it can help us to discover the hidden sides of our understanding. That is roughly how science and mathematics work.
But you know what? When we are investigating the boundaries of our understanding, we see that they all end in paradoxes, some self-referential paradoxes. Take for example, Epimenides paradox (the Cretan philosopher Epimenides of Knossos) as follows:
Epimenides, a Cretan says, “All Cretans are liars”.
Now what does this convey? Prima facie it feels like all Cretan people are liars, but then you see that person who is saying this is also a Cretan that makes him a liar, so he too is a liar. But if Epimenides himself is liar then what he said is also a lie, meaning that Cretans are not liars rather they are veracious. If Cretan’s are veracious then what Epimenides says is truth meaning that all Cretan’s are liars and this means Epimenides is also a liar. We end up in a loop, a self-referential paradox.
In the end, the sentence does not make sense, logic, the sentence is meaningless.
What happened here?
We used a language medium to create a meaning which helped to create newer understanding but that new understanding led us to bigger confusion, meaninglessness.
Here, I pose a very important question –
if the context of the sentence is meaningless does that mean that the words from which that sentence is made – words which have their own individual identity, their own absolute meaning a context are also absolutely meaningless?
What if we encounter same situation in the philosophical endeavors? as they are the building blocks our overall understanding of the creation and things beyond creation.
This is where the philosophy of deconstruction given by Jacques Derrida comes into light. I will try to explain deconstruction by building on some ideas. (you will see in the end that nothing “absolute” makes any sense or doesn’t even exist. That is also why deconstruction was rejected by many great philosophers but it has a valid point to prove.)
The flow of thought presented hereon is roughly like building an understanding and then challenging that idea because it does not present the best model of how our reality, our consciousness work.
Logocentrism
Western philosophy is based on the foundations of ‘the reason’. The Greek word logos (λόγος) literally means word, discourse, or reason. So, logocentrism considers language as the expression of reality and hence stands as a mediator between conscious and reality.
It is very important to understand that every type of understanding, knowledge building, sharing, communicating activity is associated with language. You need a medium to give a proper structure to what you are thinking and let others comprehend it. Logocentrism focuses on that.
As we have seen already that use of language in certain way could create meaninglessness, self-referential paradox, does that mean language is failing to create better truths? What exactly is happening? If language and logic is paradoxical then the reality which they are explaining must also be paradoxical but that is not the reality we live in (if it would be paradoxical, then reality would not exist, the paradoxical elements would annihilate each other)
This means that there is something lying beyond the territories of language which we are not able to comprehend and translate which could solve this paradox of language.
(Park this first thought in your mind for some time)
Plato’s definition of reality – Platonism and The theory of forms
Plato called out for “essence” of everything that exists. Essence represents that absolute truth which we try to define using ‘forms’, the forms are ideas which are non-physical, timeless, absolute. The forms create reality but they are beyond our grasp because of our physical limitations.
So, building on the theory of forms Platonism believes that in surety that there is something truly pure and absolute at the bottom – at the root of existence. It supports the existence of abstract objects which are believed to exist in the realm which is different from sensible external world and our internal consciousness.
So, when you try to comprehend the Platonism and logocentrism together, you will appreciate that language and the logic it conveys, the meaning, the context it conveys is the foundation of how we understand the creation, the philosophy itself and the products of philosophy.
Language creates an objective pivot to create absolute ideas whose correlation yields into higher truths. Language creates ‘meaning’, ‘context’, ‘logic’ according to the Platonism.
(Park this second thought)
Semiotics – Language as signs
If language is so important to understand the true reality, it becomes very important to create a structure, rules, grammar to use it effectively. Semiotics deals with these ideas.
A sign is an important part of any language, one can say that any language is made up of signs. Ferdinand de Saussure, one of the two founders of Semiology established the two components of sign as signified and signifier. As these both words are self-explanatory – signified is the one which is of interest (also known as the ‘plane of content’) and signifier is how we are observing thereby expressing the object of interest (also known as the ‘plane of expression’).


So, in written language when I am saying apple, you know I am talking about the fruit called apple which looks red, tastes tart-sweet, is crispy-crunchy in texture when one takes its bite.
(This is the third thought to be parked)
Aufhebung – the sublation
In the modern western philosophy, which considered the language as the path leading to ultimate truth the idea of sublation created ‘logical’ revolution. The language as a tool to develop logic and this logic then leading to the investigation and discovery of the ultimate truth became really vital. For logic to remain ‘logical’ one needs to define the basic objective sides like right or wrong. A given idea must be right to exist in reality otherwise, it is wrong and is invalid. We build many arguments of right and wrong to lead us to the absolute understanding. Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel is known to develop the idea of sublation. Aufhebung literally means ‘to suspend’, ‘to abolish’.
For example, darkness is the condition when there is no light. If a place is called ‘lit’ it means that there is no darkness. So, this dualism created through sublation gave the greatest philosophical power to language and thereby logocentrism. When something is not good it is called as bad, when there are enough logical arguments like such ‘binary oppositions’, one can reach to the absolute truth as far the logocentrism goes. The process almost becomes objective, self-sufficient, and mechanical, there are no chances of human error when we are handling philosophical treatise; this is the same foundation through which judicial systems created the structure of law.
(the fourth thought to be parked)
Deconstruction
What came first – chicken or the egg? meaning or language?
Just recall the four ideas which we parked before.
Jacques Derrida is the philosopher who developed the ideas of deconstruction who solved the paradox of the logic in the logocentric philosophy.
It is important to accept that wherever a paradox arises there lies an opportunity of the creation of a new branch in our knowledge system. The deconstruction is that new branch which got created here. Derrida rejected the idea of Platonism. His work in deconstruction is highly inspired from the philosophy of phenomenology. Phenomenology is the study of fundamental nature of subjective consciousness and experience.
One would get confused to appreciate the matter of subjectivity in a philosophical discourse but phenomenology presents some valid points when we are questioning the reality and developing its understanding. How can subjectivity guarantee absolute truth?
Life was always there even before chicken and egg and also in both of them
Did you get my point?
The moment we separated egg from chicken and posed them as two distinct objects the famous question about their existence in timeline becomes meaningless. In the same sense, other similar questions have exactly same meaningless fate – what is life and death? what is good and bad? what is right and wrong? what is truth and lie?
Derrida pointed out that the moment we create duality in any argument we are losing some important information which could have showed us the ‘real’ reality. Maybe reality is not just two sides of the coin, maybe absoluteness itself is not ‘absolute’. In the attempt to create purely logical arguments, we lost the possibilities to see the real context behind the existence of these arguments.
Derrida strongly promoted the idea that meaning was always there, language is just a way to convey that meaning. Using language to find out new meaning does not lead to newer meaning because this ‘structured’, ‘logical’ language has already submitted itself to the already established two sides of the result – it will either be ‘right’ and if it is not right it will be ‘wrong’.
(Now bring that first parked thought of logocentrism – idea that language is the expression of the reality)
As the logocentrism goes, language is the mediator between consciousness and reality.
Now read the lines below:

This is an example taken from internet. Fact is that every average, normal person can read and understand this. Our brain is always on energy optimization mode. It never reads each and every letter to make a meaning out of the given word, it looks at the bunch of symbols to make sense out of it. This is small example to show that meaning is more important than the symbols, signs used to convey that meaning.
If we were to strictly submit to the rules of English vocabulary and grammar, this presented sentence is senseless to all of us. That is why complete loyalty to language instead of meaning is of no use as Derrida says while explaining deconstruction.
(now bring the remaining thoughts parked in your mind)
Meaning is relative
In deconstruction, Derrida talks about how we understand anything, any idea and how logocentrism, structuralism limited our understanding. The example of scrambled words helps to identify the idea of difference – Derrida called it Différence (as in French pronunciation). Whether I call it difference in english or différence in french, you understand what I am talking about because you get the context (that we are comparing something and this is the word to establish the gap between that comparison)
When I say apple how do you know what I am talking about?
You understand that I am talking about a fruit based on the context of my speech. Otherwise, there are definitely some people who would thing of an apple as an iPhone. So, when I say an apple, you think of a class of fruits, compare other fruits with ‘this’ one, this happens really fast and we are unaware of it after some time. This is true because when I am saying apple you are sure that I am not talking about oranges or any other fruits.
When I am saying dog, you know it is dog because it is different from cats, cows, horses. You are sure of the dog ‘animal’ because it is different in some sense than other animals.
Do you see what is happening here?
Our association of given word to any object whether it may be tangible or intangible is not absolute and self-reliant. It is relative. It is built based on how it differs from another objects. This is really important to understand and appreciate when one is trying to understand deconstruction.
The logocentric and linguistic tool that we are tying to use to understand the absolute truth has its limitations of preconception. The logic has already defined its two states of existence. That is why the language based on such logic will be filled with paradoxes and will never yield newer truths.
Derrida posed validity of his idea of deconstruction by showing the limitations of semiotics.
Take speech as the language of philosophy to find the absolute truth. There is a moment in Christopher Nolan’s movie inception.


We always initiate our thinking by creating certain arbitrary point as a pivot to build logic upon it. Here, the person was told to not think about elephants and in order to not think about elephants he had first defined what elephants are – where he paradoxically first thinks about elephants – to not think about them! Did you see what happened here?
Derrida says that even though the ‘sign’ which goes as the fundamental block of language as semiotics show, it is not self-reliant, self-established. For a sign to signify something specific, it has to differ from the other objects on certain attributes, the meaning of that sign will be relative.
The Swastika used by Nazi is a holy symbol in Hindu culture which signifies well-being. (you definitely are aware of its meaning in western civilizations)

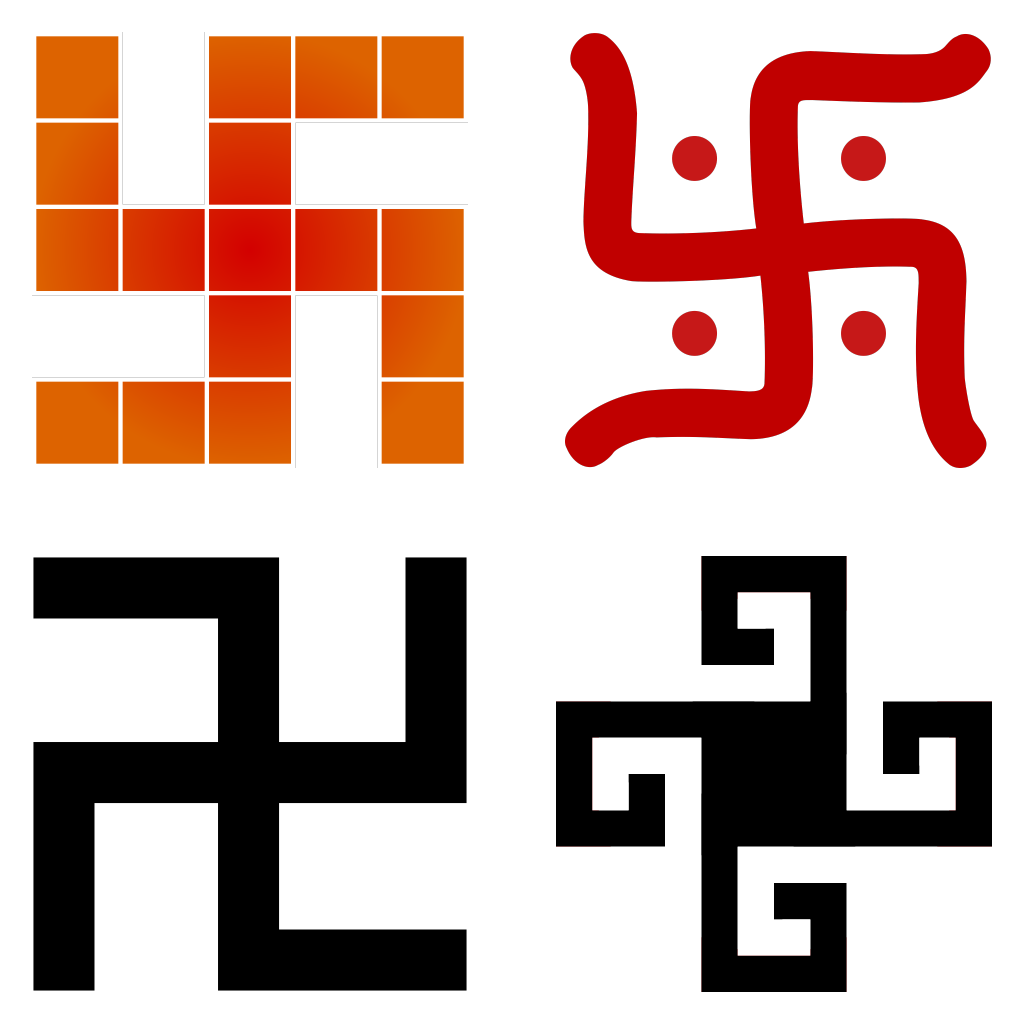
Meaning of signs is always relative, contextual.
It is our complete loyalty to symbols which misleads us, where in reality the symbols are mere media to convey the meaning, context and not the other way around. Meaning created signs, language, language does not create meaning. That is exactly why complete and blind submission to language in the pursuit of truth leads to dead end.
The purpose of language/ signs in deconstruction
(recall the fourth idea of sublation, duality in logic)
Derrida attacked the semiotics by showing its limitations.
Now, we already understand what is signifier and signified. Derrida argued that if there was no difference between signifier and signified there would not be any purpose of existence of the ‘sign’.
To explain this argument in simple words, if you are not told about the varieties in the citrus fruits, you cannot tell which one is Lemon, which one is Mandarin, which one is Lime, Pomelo, Kumquat, Grapefruit, Bergamot and Citron.
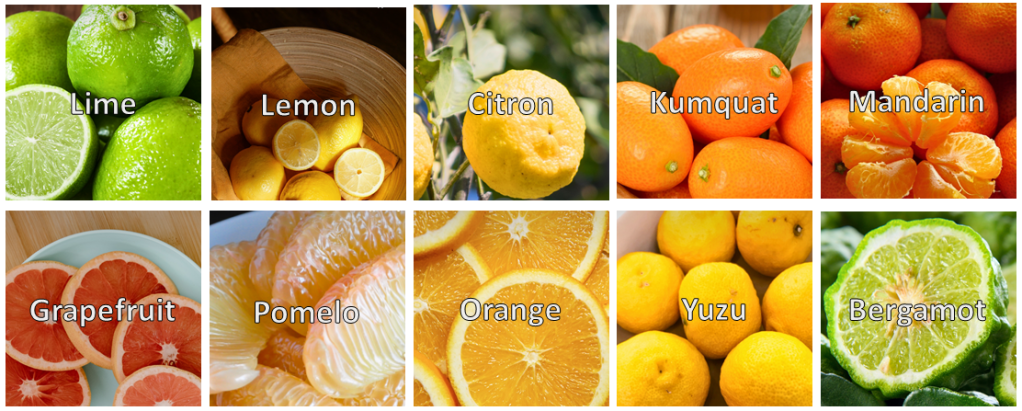

The relative difference between objects and ideas gives them their meaning. That is exactly why surrendering to strictly assigned meaning would steal the idea of its real nature. The idea would lose its other aspect due to the loss of information during formalization.
So, deconstruction shows that meaning is relative. When a sign is presented, a language is used to build an idea, it invites all its attributes and its contradictions. Again, Derrida says that blind surrender to formal attribute would never help in revealing the true nature of reality.
That is exactly why deconstruction also challenges sublation. According to deconstruction, there are never two extremes of any idea, attribute, sign. If we give into the idea of good-bad, black white, right-wrong we are losing the crucial information which lies in the spectrum that exists between these two ends. If we are able to create different levels in between these extremes of sublation we will discover new ideas.
When we talk about darkness, we know what brightness is, the relation between these two extremes helps us to understand each other. It is also true that there is some limitation in our vision which makes it impossible to perceive the constituents of the darkness, darkness is not darkness in itself, it is made up of other spectrums of light like infrared, ultraviolet. (This is just a scientific example but same can be implemented in purely philosophical treatise)

Deconstruction
So, Jacques Derrida’s deconstruction challenges the logical dualism and the purity, absoluteness of language – a powerful tool and foundation of the philosophy.
Derrida attacked logocentrism by showing the flaws in the structuralism, Derrida showed that language is actually fluid while conveying the meaning instead of being completely static.
Derrida proved his point by showing our preferences for the languages. For discussion he took preference of speech over writing.
Speech involves various modulation while expression which is not possible through writing. Even though writing has certain symbols to signify those periodic gaps they cannot replace the advantages of speech.
Now, when an overly complex idea is to be presented, in order to review the train of thoughts again and again, written language is more effective than speech. Wherever you have to ‘technically’ present a thought, written communication is better, when you want to preserve an idea forever written communication is better than speech.
This is where we realize that there is nothing like the best and the worst. Each language has its own characteristics which can be only understood and appreciated once we see the difference between them. The differences between them show that there is no hierarchy among them. There value proposition is relative.
Now the moment I bring in today’s recorded audio-visual medium which is the most popular language of documentation, writing and speech will seem trivial, but they still hold their value in certain aspects.
The meaning of deconstruction as Derrida says is to break down the language to understand what is also does not mean. Our human instinct and training in language pushes us to stick to the predefined notion of the language whereas we forget that our understanding of that very notion emerged from its comparison to other parts. Derrida through deconstruction urged that while looking at something to understand seeing what lies beyond its appearance will give you the real understanding.
Why seeing beyond what is shown is important? Because the understanding with which we are trying to interpret what is shown was never absolute, it was created only because of the difference between what it is and what it is not.
This is where deconstruction starts to confuse everyone. Derrida called this puzzlement “Aporia”.
Why the idea of deconstruction felt wrong? And is it really wrong?
The tool Derrida used to explain the notion called deconstruction itself becomes the weapon to destroy that same idea.
The very first thing to understand deconstruction is to remove the presumption which logical language, logocentrism gives that these are fully defined, singular objects which are being discussed. The moment object of discussion becomes singular, we lose the possibilities to see its other attributes. To deconstruct is to remove the preconception that there is something really absolute that we are trying to discover.

It’s like searching for star emitting only infrared light by using the camera which only works in the visible spectrum of light, because you assumed that there is only visible light and where the light is not there it is only dark. You won’t even be able to appreciate that there are some stars which emit different type of light. You presumption of duality of dark and light prevented that different knowledge of your reality. Only relative understanding of the light waves can help you appreciate that there are some waves which are different from others, which are on a ‘spectrum’.
Derrida’s ideas were controversial because most of the critical ideas in philosophy, mathematics are built upon clear distinction between objects and their fixated meaning and attribution.
Even for the word deconstruction, people attributed it to rejecting what the language conveys and accepting rather its opposite.
Deconstruction is not just breaking down any idea to expose its flaws. Deconstruction rejects the complete loyalty to the focal point of discussion while inviting the references which created our so called ‘focal point’. Most of the times our trained brain seeks for exact opposite which is where deconstruction gets misinterpreted.
Conclusion
Derrida’s basic urge through deconstruction is the rejection of the duality or presumption, and seeing beyond what is shown through the language. When we are talking about something we interpret what is our ‘subject matter’ because we know the differences between other subjects and ‘this’ subject. When we appreciate such differences the meaning becomes fluid instead of static, the thinking becomes analogue instead of digital ones and zeros. Possibilities open-up instead on being ended in the paradoxes. Whatever we are thinking about and establishing as the singular truth is inherently non-singular because it always needs its other counterparts to justify its position.
Many religious wars were waged because of remaining loyal to the religious languages, script and not understanding what they actually meant, many laws were exploited because the loopholes were discovered based on understanding only what they meant. This keeps on happening.
Deconstruction becomes very important tool to critique the ideas given in any discussion where the final pursuit is meaning and not the formality.
For Derrida’s deconstruction the ‘Aporia’, the puzzlement is not a sign of weakness rather it is the sign of maturity.
Derrida’s deconstruction thus showed that only fancy formalization of philosophy will not help us to understand the reality. We have to get rid of our loyalty to the idea that there is something really singular out there which would define everything in the end. Meaning is not what the language is conveying structurally, it is also what lies beyond that which is not conveyed. The things which are not conveyed are the line of comparison to define the worth of the things being conveyed.

“The fish trap exists because of the fish. Once you’ve gotten the fish you can forget the trap. The rabbit snare exists because of the rabbit. Once you’ve gotten the rabbit, you can forget the snare. Words exist because of meaning. Once you’ve gotten the meaning, you can forget the words. Where can I find a man who has forgotten words so I can talk with him?”
Zhuangzi, Chuang Tsu: Inner Chapters

P.S. You will appreciate the ideas of deconstruction more if you watch Denis Villeneuve’s movie Arrival (2016). The movie beautifully shows the gap between language and meaning and also how potent the ideas of deconstruction are!