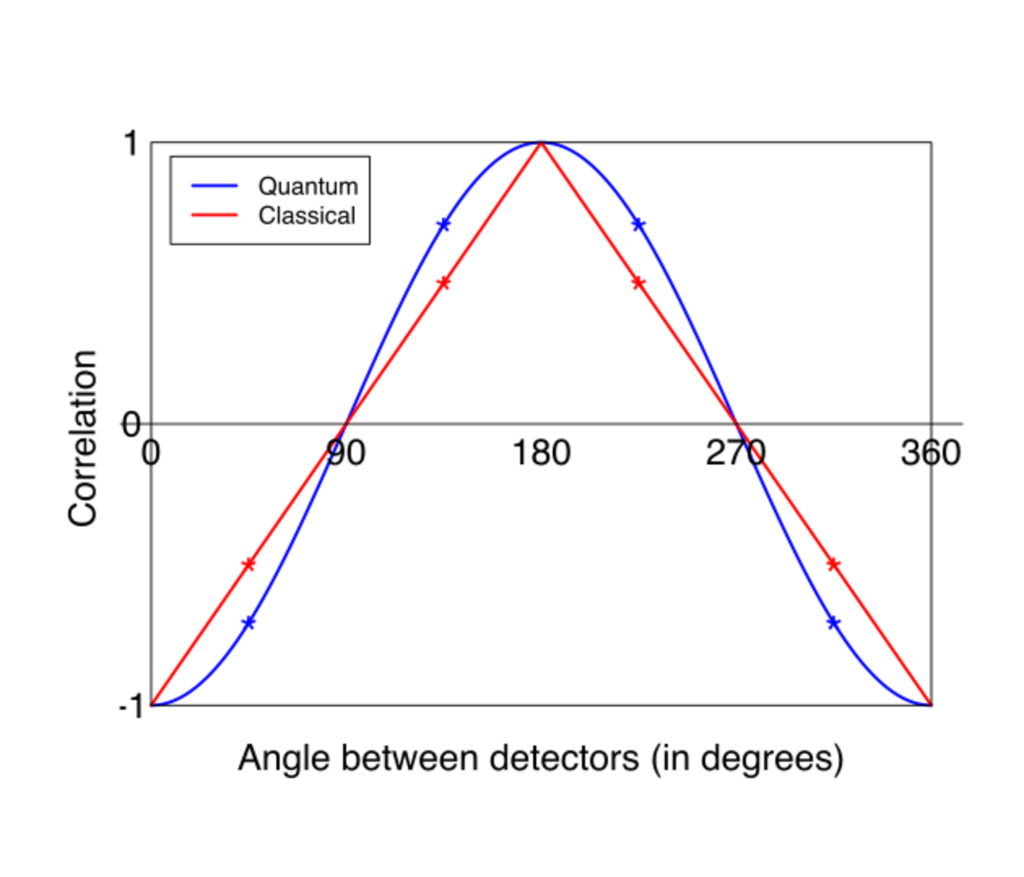
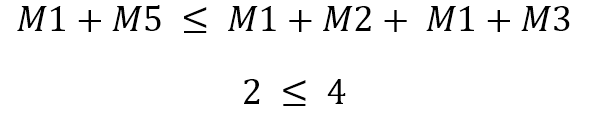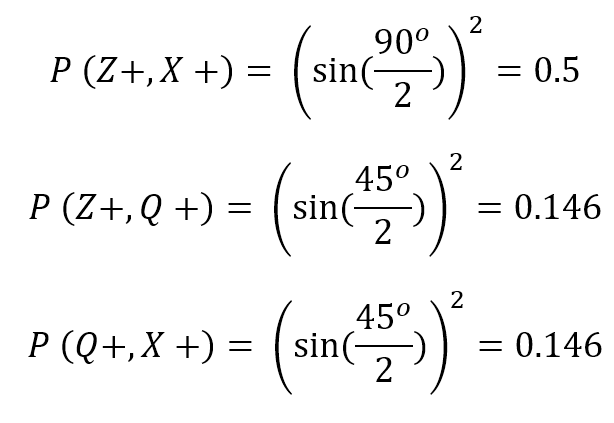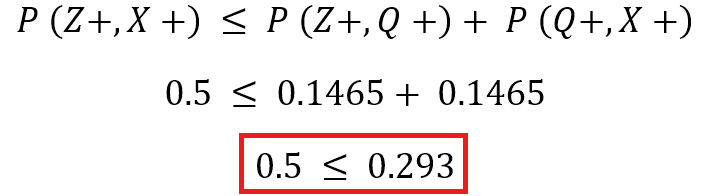Medieval Idea of Ockham’s Razor For The Modern World
Craving for Simplicity
One of the key driving factors for humans is to have complete understanding of how things work. The reason behind this is to maximize the chances of survival. Now in modern times those odds have become better. The urge to understand the working of things has been evolved into improving the quality of the survival or the existence.
The key events in the quest to understand everything that is there could be summarized as follows:
- There is some unexpected event which causes pain, suffering, loss (it can be opposite too, like extreme favorable growth, happiness, high gains. But the human tendency is to be more concerned about uncertain losses.)
Curiosity actually emerges from the urge to control everything that can be controlled and identifying what cannot be controlled and then working towards how to control uncontrollable things by understanding them in depth.
This is how we try to assign meaning to life, our very existence.
- Then we try to observe similar events associated with such experiences, record them. We try to recreate them until we have clarity on the factors which are responsible for such events. We experiment the events repeatedly so that we can have a proper theoretical understanding or a concrete reasoning behind such events.
- The key factor for the reasoning to be accepted as the practical one is its consistency with another unconnected or remotely connected events. There is some “universality” in that reason or that theory.
This is roughly how we try to understand the existence. If one asks why we are always on the quest of understanding the existence the answers are diverse.
The simple answer I think is that our brain prefers simplicity so that it can spend the saved energy to maximize its chances of survival. Our brain hates complexity because once the complexity is accepted the uncertainty has to be accepted and then the brain would start to invest its energy into those things which won’t even get materialized but could get materialized because of the non-zero probability.
Our brain craves certainty of survival.
This trait of brain to prefer simplicity might not be the nature of the reality in which it exists and tries to survive but if doing so maximizes the chances of its existence then it is a pretty much the best way.
In epistemology, the philosophy – the theory of knowledge this trait is investigated in depth. We will try to see one dimension of this thought which goes popularly as the law of parsimony and even more famously as Ockham’s Razor
William of Ockham and Ockham’s Razor
William of Ockham was an important medieval philosopher, theologian who brought the law of parsimony into the focus. Although the idea was already in existence from Aristotle.
Aristotle believed that nature always works in efficient ways possible and thus the explanation for the events in nature ought to be the efficient ones.
Although Medieval, Ockham’s razor is one crucial idea in the age of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.
Ockham’s Razor emerges from his writing called “Summa Totius Logicae” exactly as:
“Pluralitas non est ponenda sine necessitate” meaning “Plurality should not be posited without necessity”.

In modern Science, philosophy, the idea “simply” goes like this:
“Do not mix unnecessary things”
OR
“All things being equal the simplest solution is the best.”
Consequences of Ockham’s Razor
The principle of parsimony (lex parsimoniae in Latin) thereby Ockham’s Razor helps us to not complicate things when we are investigating them. It is used as a thumb rule or heuristic to generate theories having better predictability. The moment we are saying that the preferences should be to ‘the simpler theory with better predictability’ is the moment when people most of the times misinterpret the Ockham’s razor. Razor implying that chopping off everything unnecessary, if not chopped would contribute to the increase in the complexity thereby compromising the predictability. We will see how Ockham’s Razor affects positively and negatively when we are trying to understand the things around us.
Good consequences:
Search for the theory of everything
Aristotle’s belief that nature always chooses the efficient route to decide the fate of anything reinforced the idea that the theories which would explain the nature are the best if they involve the least possible variables.
Einstein’s theory of relativity and the equation of energy connecting to the mass is the best example to explain this. An elegant equation with mere 1 inch length encompasses all the big secrets of the universe.
The theory of relativity is elegant in a way that it covers Newton’s understanding of motion and gravity and furthermore extends it to the understanding of the black holes where Newton’s same theory would become limited.
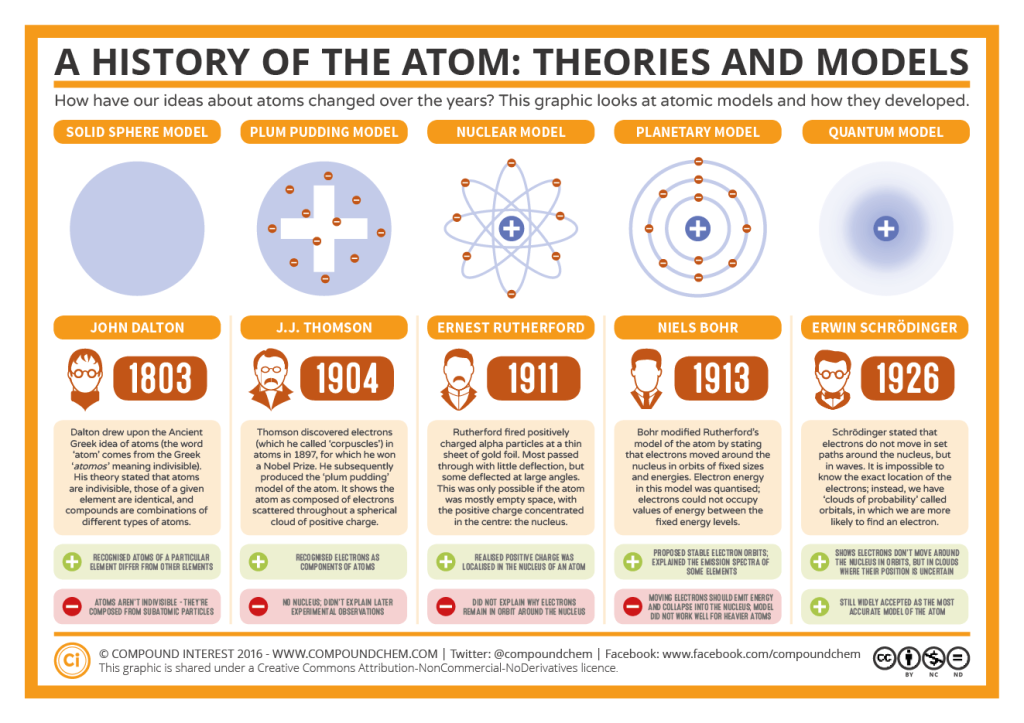
Quantum mechanics explains everything that atom can create. It justifies why the earlier models of atoms were perceived in those particular ways (like atom being a solid sphere, a plum pudding, a thing with nucleus at center and electrons in their orbits).
Quantum mechanics thus is the most efficient way to explain what we observed and why we interpreted those observations in a particular way. Please note that the goal is not to falsify something, prove something wrong; the goal of knowledge or science is to understand why we theorized something in wrong way and why it doesn’t align with the reality we are trying to observe and understand.
Efficient Machine Learning Models – Generalization Error
In the age of AI, the efficiency of Machine Learning Algorithms is one crucial decision maker of the investments to be made to evolve it further. The key goal of any Machine Learning algorithm is to create a mathematical equation (or layers of mathematical equations) which would understand the data provided, make sense of it and now predict the outcomes after understanding the data.
This sounds simple while establishing theoretically but the real-life data one provides ML algorithms is filled with variety of noises – unwanted, unconnected, irrelevant data points.
If the ML algorithm would try to fit the noise too, it would add too many variables in its mathematical equations. Now the model would fit each and every data point but at the same point it loses confidence to predict the outcomes because the noise is not really connected to the system one is trying to define.
That is why a complex ML algorithm fitting all the data points (R2=1) is an ideal situation – ideal meaning practically impossible because it is exposed to a very limited dataset. An ideal ML algorithm has a “generalized” idea of the data points on which it was not trained. Meaning that this ML algorithm has such an effective understanding of what is happening in the dataset with least number of equations that it is now able to understand what could happen if something is to be predicted outside of its training dataset (Q2 – algorithm’s ability to predict the unseen data – should be maximum). L1, L2 regularization techniques used in ML are example of that. Now the ML algorithm is not just interpolating proportionally the points in between, it has its own mathematical justifications to decide whether and how to interpolate aggressively or not – in order to predict the realistic outcome.
Ockham’s Razor thus proves to be important in the age of AI to select efficient algorithms, efficient algorithms ensure efficient use of power, resources thereby the investments.
Parsimony in Psychology – Morgan’s Canon
In very simple words, I would say three words to explain what this means – “Life of Pie”.
The movie Life of Pie has a moment when Pie’s father tells him that the emotions which Pie is seeing in the Tiger Richard Parker’s eyes are mere the reflection of how Pie feels the tiger would be feeling i.e., hungry in that specific case.

In animal psychology (Comparative Psychology) researches, Morgan’s Canon asks scientist to not over-attribute any human quality that humans possess to animals without any concrete basis.
“In no case is an animal activity to be interpreted in terms of higher psychological processes if it can be fairly interpreted in terms of processes which stand lower in the scale of psychological evolution and development.”
The scene from Life of Pie strongly resonates with Morgan’s canon.
There is a reason why Morgan established this idea. We humans have a tendency to see human form in everything that is not even human – this is anthropomorphism. While studying animals, these anthropomorphic tendencies would mislead each and every study because other animals and human share many common things. Unless there is no strong evidence to justify the human like intelligent behavior the simplest explanation should be selected to justify the behavior of the animal in their psychological studies.
These are some of the examples where Ockham’s razor proves to be very valuable.
Bad Consequences (limitations of Ockham’s Razor)
There is other side to simplification of things, we will now see how people misinterpret the principle of parsimony thereby Ockham’s Razor.
Universe might prefer complexity to exist
In the pursuit of the theory of everything, Einstein himself was confused that “how could God play the dices?” How can one bridge the gap that exists between the theory of relativity and the quantum mechanics. One explains the heavenly objects and the other explains what lies at the bottom of the bottom of particles which make the universe existent.
One will realize that there is more than what we are using in current theory which needs to be considered to explain the reality in a better way.
One reason why Einstein was genius of all times is because he knew that something was missing in his theory. He was not ashamed of the complexity the theory of everything may carry. Even while speaking about his elegant theory of relativity Einstein had this opinion:

Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
Those who are actually working in the field of AI would explain this to you that how difficult it is to create an Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). Even though we have some of the greatest chat-bots, AI assistants, AI agents, they are experts in executing specific tasks only. They can immediately get biased, they can be fooled easily, bypassed easily.
The key reasons behind these shortcomings are many. The AI tools perform the best when they are designed to perform specific tasks, they lack common sense like the humans do, they lack the emotional dimension in the decision making (one of the important aspects of how humans generalize the understanding of their surrounding), they cannot directly build the bridges between their algorithms unless enough data is provided. AI doesn’t have intuition which humans have developed over the thousands of years of natural evolution.
It is also important to understand how greatly we underestimate the computation and decision-making capability of our brains and how much power it takes to replicate the same in machines.
So, maybe complexity is prerequisite for AGI and thus the enormous number of resources that will be required to achieve it.
Human like intelligence in Animals
The story of Koko and Robin Williams could be good example to explain this. Koko – a female gorilla was trained in American Sign Language (ASL) by Francine “Penny” Patterson. Penny called this language as Gorilla Sign Language (GSL).
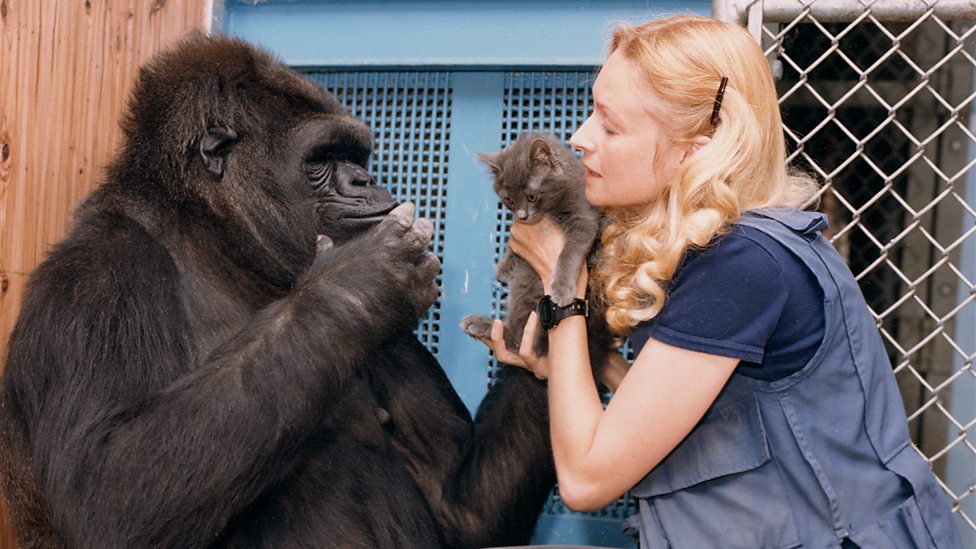

There is a very famous video of the meeting between the movie actor Robin Williams and Koko. Soon after the death of her gorilla friend Michael, Koko met Robin Williams and she laughed after a long time along with Robin, she played with him, she even recognized Robin from his movie cassette cover.

When the instructors of Koko told her about the death of Robin Williams, she expressed her grief by signaling the instructors if she could cry, her lips were trembling in grief. See the emotional depth she had just like normal humans do.
Dolphins are also one good example to demonstrate human like intelligence in animals.
This means that Ockham’s Razor, Principle of parsimony or Morgan’s canon are of no use. What is happening here? What goes missing during the oversimplification? What are we misunderstanding?
What goes missing in simplification?
The main problem with Ockham’s razor or its any other equivalent philosophies is the convenience they bring. Just like by collecting a biased data you can actually prove anything wrong which in reality is right, in the same way people misinterpreted the principle of parsimony.
The key reason for William of Ockham to support the principle of parsimony was because he was a nominalist. “Nominalism” says that there is nothing common between anything and everything that is there in reality. Everything has its own individual nature and what we see common in many things collectively are just the ‘names’ given to them. The red which we see in blood and in rose is just the name of the color and there is nothing like red which actually exists on its own.
This means that the color which we see in things, there is no such thing as color in its absoluteness, it is just some signal our eyes generate to tell brain the difference between the light absorbed and light reflected or the temperature of the surface of the object.
So, William of Ockham posed that as everything has its own attributes individually, when you are trying to create a philosophy for a group of things, you should consider only those individual attributes which are necessary to create a theory.
(William of Ockham himself drifted away in his ideas of Parsimony and Nominalism; I will discuss that specifically in the Philosophy of Nominalism next time.)
What people still misinterpret today when they talk about Ockham’s razor is “to select the simplest explanation to things”. This is not what he meant actually.
Same is the story with Morgan’s Canon. Morgan’s main intent was to have a concrete justification when someone is explaining human-like behavior in animals. His idea was that the conclusions should be reasoning-based and not based on the observation that animals in the study had that specific type of intelligence. The idea was to observe without any preconditioning, prejudice or any impression or expectation.
I have already explained how Einstein was a genius; he was very well aware that during creating the very elegant understanding of the universe he might have missed something on the expense of simplification.
The standard mathematical model in particle physics looks like this (maybe sometime in future I will be able to appreciate and explain it to its core):

Context is everything
Now you will be able to appreciate why Ockham’s razor is a tool and not the final truth. People exploit Ockham’s Razor to demonstrate their philosophical grandeur and simplify the meaning to their favors consciously (sometimes unconsciously).
What people ignore is the purpose of the chopping unnecessary parts in any process to develop understanding, philosophy or theory. The goal was never to simplify things, the goal was to remove things which would interfere in the process of testing our hypotheses.
People most of the times miss the point of parsimony which is to make a realistic attempt to check how and why our understanding of things which we have and the real nature of things differ, how can we fill the gap between what we theorize, what we can test and what real there exists.
Context thus plays very important role in every pursuit of knowledge, even in the knowledge of the self. It is important to understand the boundary conditions of our knowledge. One should know where their beliefs (even if they are true) can be limited, can be challenged, can be difficult to prove because what we know is just a drop, what we cannot know is ocean.

I think what people miss in simplification or parsimony is the context and context varies from situation to situation.
Scientifically, Newton’s laws of gravitation have no problem when we are talking about our solar system. In fact, they are so accurate that modern space missions still rely on these laws. There rarely is any need to use the science of black holes in most of such missions.
The context is the precision of deciding the trajectory of objects in solar system.
But, when it comes to Global Positioning System (GPS), the theory of relativity becomes important. The bending of space time due to earth’s mass and the slowing down of time for navigation satellites from it and the time adjustments for atomic clocks at these two points matters a lot. Newton’s laws cannot explain that.
The context is how precise can the time be measured and how the difference in time can be connected to the understanding of the position of the object around the globe.
It is very easy to demonstrate how Ockham’s razor still remains important in scientific community and how scientists are aware of its limitations.
It becomes problematic when we try to understand and justify life with it.
The problem is that we get to decide the context (most of the times)
Call it a blessing because scientific community is always in the state of its own renewal because it relies on objective evidences, but it is still not immune to missing context or wishful context. (The falsified biased scientific studies published to create confusions are best example of that.)
The best example of losing context while still being scientific or unbiased is the Debates on News channels or any debate (sadly) that exists on popularity. Soon you will realize that the context of most of such debates is to entertain people, create controversies and not find the ultimate truth or facts.
In the very opening of this discussion, I had explained how our brains try to optimize processing to save energy for better tasks to guarantee better survival. The death of our own beliefs, our identity is also failure to survive. Psychological, ideological death is as equal as the actual death, maybe it is more painful than real death for almost all of us. Religion is one stream of such ideologies where people are ready to die physically just because the religious beliefs, they live for should remain alive. Most of the people are scared of mathematics not because it is too complicated, they fear math because it shows them the vulnerabilities in their process of step-wise thinking, same people can be expert dancers, master artists, master instrument players which involve rather more complicated mathematical manipulations – music in a simple way is manipulation of certain sound wave-forms. The music theory, harmony, color theory, physiological manipulation of body with the rhythm, and sound are all purely mathematical concepts. It’s just that we don’t want ourselves to remain in the states of vulnerabilities for longer times. It’s equivalent of exposing cover to our enemy thereby reducing our chances of survival.
The thing is that the tendency of nature to choose the path of least resistance gets reflected in our own nature too. Which is why simplification and Ockham’s Razor seems attractive. But at the same time, we forget that it is the same nature whose deliberate and continuous actions against the adversities made us who we are, made impossible things possible for us.
Daniel Kahneman has explained the two cognitive systems our brain uses in his book Thinking Fast and Slow.
System 1 is fast and intuitive good for repetitive tasks but bad at finding biases, errors, hostile to new and complicated scenarios.
System 2 is slow and deliberate for analytical and reasoning-based tasks but is not effective for routine tasks.
The people who exploit Ockham’s Razor (even William of Ockham himself! – this story will show up in post on nominalism!) are oversimplifying things because the belief they have is justified through it. It will stand some limited tests but the moment it is exposed to universal tests they fail. And that is how religions, sects, faiths operate when they are blinding people from the real truths. I am not saying religion is bad, I am saying how objectivity in religion can be used to show its scientific nature and still fool the people. Same can happen in scientific communities, all of the pseudo-scientific concepts are one great examples of that.
Now you can see the problem. People want to create understanding of the surrounding not because they really want to understand it. They want to do it because it will feed the beliefs they already have and Ockham’s Razor or the principle of Parsimony is a great tool to facilitate that. In the end, it is just a tool. How it impacts the creation is solely based on the intent of the one who is using it.
That is exactly why when you are questioning something or are standing against something or supporting something ask yourself this one question:
Are you doing this for understanding the reality or to feed your own wishful picture of reality?

So, whenever you are trying to understand something make sure that your context is to really understand the thing and not expect it to be in certain thing you wish. Remember, you are the controller of the context and it is very easy to fool ourselves.
Further reading: