Coming out of the Dunning-Kruger Effect
Many a times google searches are the final resort to end debates or any conflicts. Such common debates among our friends/ relatives/ acquaintances mainly require third party confirmation because both sides are adamant on their opinions. You will notice that even when a practical and reasonable argument is placed in front of the person, he/she will not accept that argument and stick to their opinions. Have you wondered why does that happen? The internet, media, “Whats App / Facebook universities” have developed enough “facts” on everything by consistent bombarding of the information and curated, person specific, behavior specific content that everybody has opinion about everything. Most of the times, peoples consider themselves expert of the field while presenting such opinions.


One more question, is their certain group of people who are susceptible to such level of stupidity due to ignorance? The answer is No.
Turns out that everyone – literally everyone of us is prone to such stupidity, lack of knowledge and ignorance.
We are what make up of our decisions. Such confident ignorance creates more chaos in the information and knowledge we have thereby may affect our decision-making process. And this ill-information, ignorance and our confidence for it reveals its devilish nature when the decisions are very crucial, life altering. No wonder someone has already said that “Half-knowledge is dangerous!”
Dunning-Kruger Effect explained in Psychology has some interesting findings on the relation between our competence and confidence about our knowledge. We will see how it may help us in understanding the nature of how we understand what we know and what we don’t know.
The Dunning-Kruger Effect
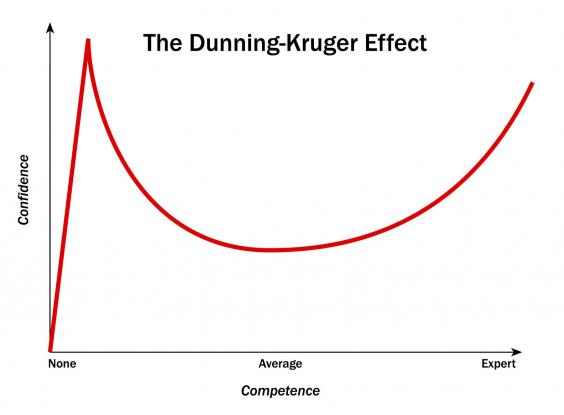
Psychologists David Dunning and Justin Kruger identified a cognitive bias in people across various fields. They asked people to evaluate their expertise in certain fields and asked them to rate themselves accordingly. One of the highlighted and most famous result can be shown as below:

There are two immediate things that we can understand from this graph:
- Those belonging to low competency group perceive their knowledge greater that their actual knowledge. They consider that they know more even but in actual they know less of it. Seems like they are overconfident about what they know.
- The area where the graphs cross each other is even more interesting. Those belonging to high competency group under-calculate their competency. Even though they have more competency, more knowledge than others in reality, they still think that they don’t know enough. They are not confident about what they know.
This result reminds me of the quote by Bertrand Russel.

The whole problem with the world is that fools and fanatics are always so certain of themselves, and wiser people so full of doubts.
– Bertrand Russel
The Double Burden of Ignorance
Dunning-Kruger Effect is more associated with the overconfidence that less competent people carry. The effect associated with the lack of confidence in more confident/ expert people is associated with the effect called “The Imposter Syndrome”. People with imposter syndrome consider that they are this fake person acting like they are genius/ expert and the “fake”-ness may get exposed sometimes even though they are genius in reality. They think that what they have achieved, known is not enough.
So, one can say that the Dunning-Kruger Effect is the opposite of the imposter Syndrome.
In single sentence the Dunning-Kruger Effect can be summarized as below:
“The ignorant people are ignorant of their ignorance.”
This is also known as “the double burden of ignorance”. Dunning and Kruger explained their interesting idea about our awareness about our own knowledge in this way- The less competent people – the ignorant people carry double curse. The first one is that they actually don’t know enough about something. The second one is that this lack of knowledge makes them think that they have known everything that there is to know. The lack of knowledge blinds them from knowing beyond what they know, thereby shunting their search for knowledge.
“Ignorance often refuses rather can’t recognize itself”
David Dunning
This is sometimes known as “The Illusion of Superiority”. Such, confident but incompetent people are always susceptible to two immediate regrets while making decisions.
- They make mistakes based on the less information/ less knowledge they have and reach poor decisions.
- This lack of information further prevents them from acknowledging and further correcting these mistakes. And the cycle further feeds itself.
The Roots of Dunning- Kruger Effect
The first cause is apparent in the double burden of ignorance indicating that lack of knowledge/ expertise bounds the definition of what the real knowledge/ expertise is.
The second one is hidden in our confidence about anything. While living in the social construct, it is mostly true that the confidence has huge impact on our decision making. People believe more in confident opinions rather that their truth value. Confidence brings certainty thereby predictability which calms our minds from the chaos of the decisions and their consequences. People always like certainty and confidence gives you that.
No wonder people say that:
“Bad confidence and Good Confidence both are same- The Confidence”
Thus, incompetent people are always confident about what they know about things and also believe that there is nothing more to know which brings the comfort to their mind.
One more reason is hidden in our upbringing and the environment around us. Student reading same books for the exam perform differently. It is because of the ways in which they construct the ideas provided by the book in their mind and this is dependent on how we think, what are our basic ideas about everything. Our thinking, our basic ideas are directly affected by our environment, upbringing, culture, parenting, companions which are totally random in every sense.
In addition to this, we tend to take mental shortcuts while knowing, understanding anything, thereby cementing the ideas of knowing everything immediately. Simple example is the digital display. Even though the display has minute pixels of three colors only- we collectively perceive it as a whole object, whole picture of something totally different. Our brain always tries to fill the gaps in what we see and what we know. This is not just for incompetent people rather this is true for every single human being.
If we do not question what we know about something and carelessly build our understanding around it then, such knowledge can be easily defeated. Which is highly possible in people with dunning-Kruger effect.
Metacognition and acknowledging our ignorance
So, if our ignorance blinds our awareness of the ignorance itself, then how can we overcome this?
One part of the answer is hidden in “Metacognition”. Metacognition is the awareness of one’s ‘ways thinking’ and ‘knowledge building’ by finding the patterns during such thinking.
There is one interesting concept called Johari Window which can be simply put in the following picture:
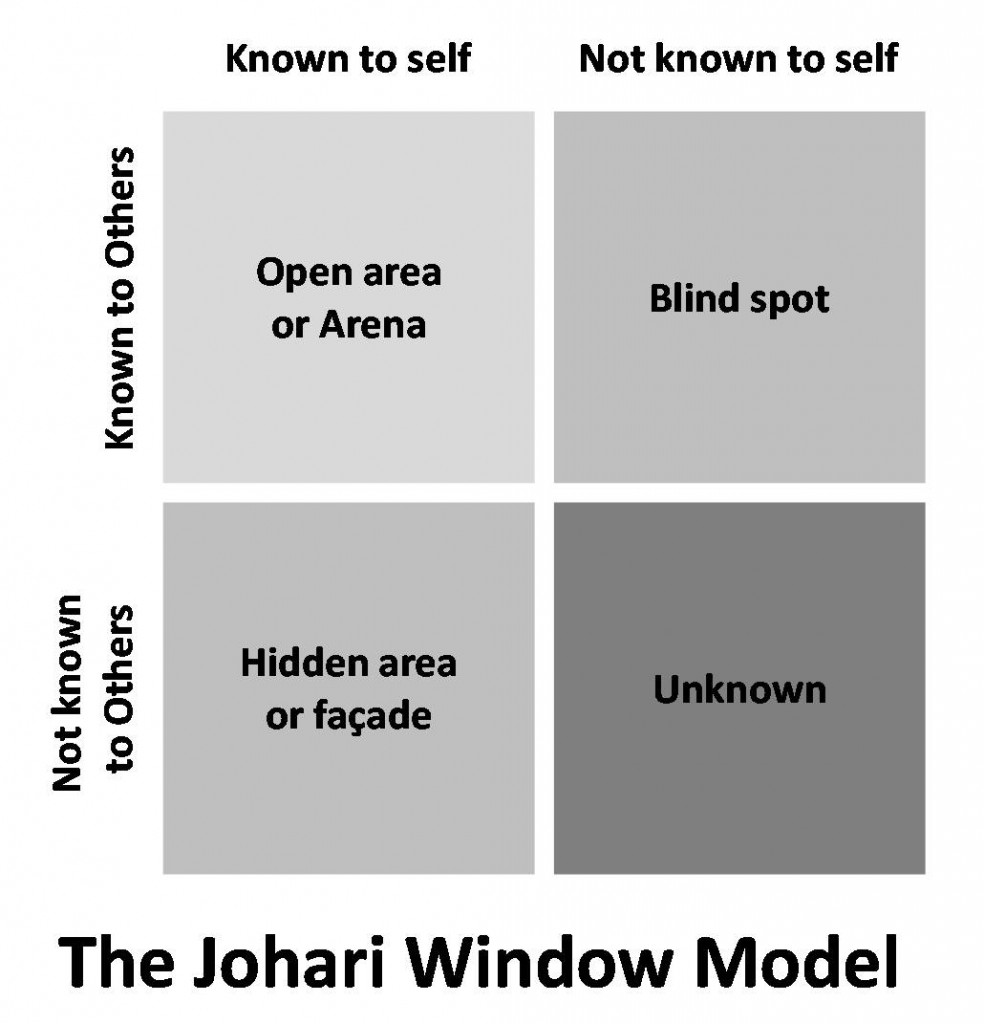
There are four parts of yourself:
- One that is known to yourself and others – everyone including you are aware of it
- One that is only known to you and not others – only you know about it
- One that is known to others but not to you – others can see that in you but not you
- One that is neither known by you nor by the others – the real unknown
This concept was developed by psychologists Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham (Jo from Joseph and Hari from Harrington) in 1955. The Johari Window is used to explain how we interact with each other and have relationship with each other.
The Johari Window focuses on improving the relationships by expanding the “Open Area” or “Arena” using feedback from surrounding. Johari Window is mostly referred to explain our social interactions and relationship building but it can show some directions for escaping out of the Dunning-Kruger Effect.
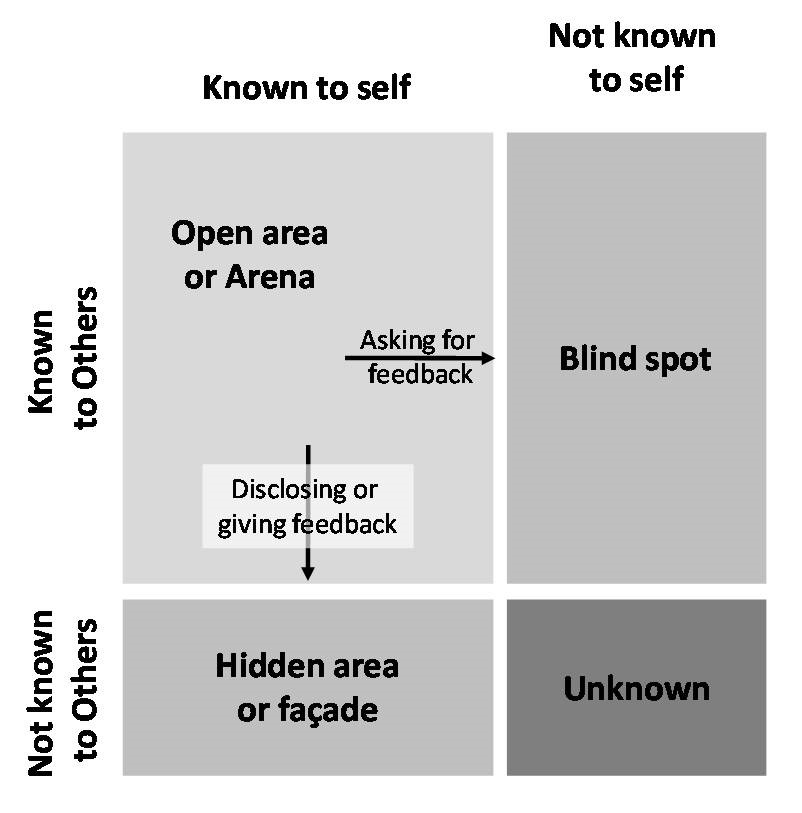
In similarity to our personality or its awareness, there are four types of knowledge:
- Known knowns: knowledge that you can know
- Known unknowns: Knowledge that you know exists and is beyond your reach/ understanding
- Unknown knowns: Knowledge that you have already but you are not aware of it
- Unknown unknowns: That which is not known and cannot be known
The Intellectual Humility
The second part lies in “Intellectual Humility”.
- The “Known knowns” type of knowledge is already established and uniform throughout the people.
- The “Known unknowns” type of knowledge cannot be known completely which needs one to accept the bounds of his/her own understandings and the uncertainty of the knowledge that comes with it. It’s like making peace with what you cannot know and keep on improving it. The known unknowns can be understood by feedback and remaining open to ideas. Understanding what the experts of that field know. The “real intellectual humility”.
- The “Unknown knowns” type of knowledge is revealed when you interact with others and thereby understand what others understand. It’s just you have it already but when you see others doing it you realize that you can do it too.
- The “Unknown unknowns” type of knowledge is more susceptible to Dunning-Kruger Effect. Where the double burden of ignorance is highlighted. The intellectual humility is the only way to get out of it.
In short, there can be four important ways to overcome Dunning-Kruger Effect thereby our ignorance. Humility, Feedback, Criticism and Curiosity are these four ways. Humility will help to know more there is to know and understand limits of your knowledge. It will also give the perspective for others’ opinion and the reason behind it. Feedback thereby positive comparison from/with others will help to know what you lack and focus on to build upon it. Criticism will help you to catch up with experts (given that they are free from Dunning-Kruger Effect!) and Curiosity for everything will help you to develop new perspectives while keeping your feet on the grounds.
“The more I know, the more I realize I know nothing.”
Socrates
(Note-The famous graph used to explain the Dunning-Kruger Effect are not even present in the original publications by D Dunning and J Kruger!)
References and Further Reading:
- Kruger, Jacques and David Dunning. “Unskilled and unaware of it: how difficulties in recognizing one’s own incompetence lead to inflated self-assessments.” Journal of personality and social psychology 77 6 (1999): 1121-34 .
- Chapter five – The Dunning–Kruger Effect: On Being Ignorant of One’s Own Ignorance, David Dunning, Advances in Experimental Social Psychology
- The Johari Window Model – by http://www.communicationtheory.org
- The Dunning-Kruger Effect: The Paradox of Our Own Ignorance by Mark Manson
- What Is the Dunning-Kruger Effect? by Kendra Cherry on http://www.verywellmind.com
- “Why ignorance fails to recognize itself” Featuring David Dunning by Macmillan Learning