Anxiety’s like a rocking chair. It gives you something to do, but it doesn’t get you very far
Jodi Picoult
Survival, Fear, and Anxiety
Every living thing if not have any goal in their lifetime would at least have sole goal of existing, surviving. Nobody wants to die and all of us always yearn to live forever but we know our limitations and hence are always on the quest of justifying the finite existence granted to us. Even if we are certain of the end closing in, our instincts are evolved in such way that many of the times, we bear the ability to cheat death. Humans have further extended cheating the death using science and technology. Technology augmented our lives, reduced the risks of death, created a safe environment to grow, increased our chances of survival.
The fear of death and uncertainty of future is the key driver in our improved survival instincts and excessive use of technology to achieve it. We plan for things in advance, create backup plans if something would go wrong, have risk assessments before the execution, understand and decide according to the cost benefit analysis. That is what makes us humans and also separates from other species (although rest of the surviving species are also smart in their own ways to increase their chances of survival like viruses – but hopefully humans have other ways to overcome them)
So, fear in a way triggers the actions to ensure survival. Anxiety – a sophisticated form of fear which prepares us in advance even before the fear causing scenario is supposed to happen. Simply put anxiety is an anticipatory type of fear to increase the chances of survival.
I am talking about fear and anxiety because they are bugging my mind for many days. Recently I watched Inside Out 2 movie and the it really delivers. The narrative has successfully presented how all emotions play a vital role in creating our personality in whole. Anxiety was new and important emotion presented in this movie. Every moment where anxiety came in focus it was fully relatable to me. Once I was done crying in the end the anxiety never left me (figuratively!), I felt a strong urge to understand the anxiety on deeper levels and what the domain experts have to say about anxiety.
The discussion heron is not a movie review rather I have made some attempt to summarize what the real-world scientists have to say about anxiety. I won’t be giving you the tricks, counseling and recommending any medicines to cure anxiety disorders. (Trained professional, experts are the best people to do that – “I AM NO EXPERT”)
My focus of the discussion is to question why anxiety exists in first place when we have an emotion called fear, another question is how to interpret the anxious emotions and what leads to anxiety disorder, where does the root of anxiety lie and is anxiety a bad or negative emotion? If it is so then why? and if not – then why?
While posing such questions and researching articles I came across some beautiful ideas, experiments and theories established by professionals in the field. I will throw light on these ideas in the coming discussion.
The fear is real! – is it? – Defining anxiety
As I already mentioned that fear of death, the unknown and urge to live long are always fighting with each other. Humans rather every species existing today in nature mastered this battle to some extent and have ridden on chariots of evolution to augment – change themselves to adapt with the surroundings and improve the chances of survival.
A deer completely aware of its surrounding, grazing in the open grass fields can distinguish the rusting of leaves due to winds and rustling due to sudden movements of an apex predator like tiger. When the exams are on top of tomorrow, we are ready to sacrifice the night sleep to crack them (engineers would resonate more with this!) We know that the pain of failing, fear of failing is worse than painfully covering syllabus overnight! The fear is there and the anticipatory response is also there, only the level of sophistication is different.
Why I say sophistication? It is because due to the advancements in our lifestyles humans are rarely exposed to the real life-threatening scenarios like animal do (still today). Our fears are now more anticipatory. I would say most of our fears are now classified as anxiety.
Wikipedia goes like this for anxiety –
“Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events.”
So, the key differentiating aspect between fear and anxiety is the anticipation. Anxiety is a prospective emotion and a forward-looking emotion. Whereas fear is the emotional response to current threat. Fear makes us act immediately; anxiety keeps us ready for future threats. Fear will immediately decide fight or flight whereas anxiety will create plans, strategies for both and also calculate which one is more probable. (now you can appreciate why anxiety is more intense in over-thinkers, the analysis paralysis is one mild example of this.)
Anxiety is also an emotion important from evolutionary perspective as it has helped the current existing species to remain existent. The ability to anticipate future and preparing for it in advance gives competitive edge in survival.
Why Is Anxiety Good?
While reading about anxiety I came across a very good paper by Dr. Randolph M. Nesse.

Randolph M. Nesse is a Professor Emeritus of Psychiatry and Psychology in University of Michigan. The ideas and theory he created to understand and identify anxiety and its intensity are very important and interesting.
Dr. Ness developed the smoke detector principle to control and quantify the medication used to fight with anxiety disorder. (He poses very simple but important question the opening of the paper that “Is he medicating his patients too much? is he harming them?”) The fundamental doubt Dr. Ness had was if the anxiety is evolved during evolution to improve our chances of survival, then why are we forced to reduce its symptoms and effects? Why are we using medications, therapies to reduce these symptoms, effects of anxiety. What if the patient is too anxious for given thing and that thing is too real to happen but the doctor dumbed that emotion down? (Dr. Ness calls it down-regulating the mechanisms causing anxiety)
The core of his thinking is that if we keep on “down-regulating” our anxiety which is an evolutionary gift to us, we might never be able to gauge the future in better way and prepare for it in advance to improve our chances of survival. (this is an exaggeration of the scenario but it proves a point)
This calls for the quantification of anxiety. Which Dr. Ness did through the smoke detector principle.
The Smoke Detector Principle – How Much Anxiety Is Too Much?
Dr. Ness in another paper talks about the mechanism which is a feed-back system between the animal and its surroundings, which selects the emotional response to improve the chances of survival. The emotions we have today are the result of such evolution to maintain “homeostasis” – the balance among our bodily system to survive and function properly.
According to his ideas, anxiety works like a smoke detector.
The anxiety response is always trying to maximize the chances of survival and escape from a life-threatening situation. When we set a smoke detector it will go off even when the fire is not that extreme or if there is just some smoke which can be a controllable one. The smoke detector is designed to never miss a single fire causing situation. This ensures complete confidence in smoke detector that it will save people from every life taking fire scenario. But, it’s the same mechanism of smoke detector which forces people to evacuate frequently even when the fire or smoke where controllable or life threatening.
The frequent emergency evacuation even when it is not required is the same problem with the extreme intensity cases of anxiety. Always having armor ready for combat may sometimes make the soldier to lose the agility.
The patients with anxiety disorder have lowered sense of real threat. Their system triggers too many false alarms.
Dr. Ness established various techniques to quantify the levels of anxiety. The responses from anxiety include increased heart rate, rise in certain bodily chemicals – stress hormone secretion which can be easily measured as signals using instruments. Thus, the smoke detector principal paved a way to quantify the anxiety and understand what triggers the anxiety disorders in patients. It helps to understand how and why a level of anxiety is healthy in normal person and what level of anxiety is unhealthy and needs drug administration, therapy, how it can be administered by altering the setting within and around the person.
The core reasons why we need not to be intensely anxious about common life threats are as follows as Dr. Ness explains in his papers:
- Regulatory mechanisms have tendency to make errors and be extra defensive about situations
- We do not need to always be extra defensive to avoid given threat. (A machine gun in a bulletproof enclosure is not required to kill a mosquito.)
- Our body and surroundings have multiple layers of defense for almost all common threats. We are evolved and have survived in that way.
- Our environment is much safer than it was at the time we evolved

Types of Anxiety Disorders
Now that we have understood what is the nature of anxiety and what is its mechanism. Here are some important anxiety disorders to outline. Huge amount of information is available in literature, internet websites on these:
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) – too much worrying about ordinary things, problems like money, work, health, relations, family, and anything possible or imaginable, it may not exist in reality.
- Hypochondriasis – People suffering from this often worry about the health condition when nothing is wrong with their body. The word comes from feeling of stomach pain the person experiences even when everything is alright.
- Specific phobia – fear of anything but specific without any reason. It’s the fear for certain thing even when it does not pose threat.
- Social anxiety disorder (SAD) – In this scenario people intensely fear the public situations, humiliations, embarrassments, criticisms.
- Separation anxiety disorder (SepAD) – People in this case intensely fear the loss of person or a place
- Agoraphobia – it is fear of being in situation where there is no exit door, or escape strategy. Fear of using public transportation, being in large crowds are some examples.
- Panic disorder – these are outburst of all the collective or intensive fears, they come quickly and last for short time.
- Selective mutism (SM) – in this case the person is extremely fearful of initiating a conversation, does not speak to specific people or in specific situations or conditions even when they are forced to talk by humiliation or mocking.
Post traumatic syndrome disorder (PTSD) and Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) were once classified under anxiety disorders (now not under anxiety disorder in DSM – Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of mental disorders)
Signal Detection Theory For Interpreting ‘Anxiety Like Responses’
One good paper in the Canadian Journal of Psychiatry by Bateson et al. shows how the smoke detector principal can be used to decide the boundaries of different levels of “anxiety like-responses”. This paper talks about signal detection theory and optimal threshold. The beauty of this paper for me is the mathematical model it establishes to explain psychological events. A single formula will help you understand the difference between normal anxiety and anxiety disorder.
With the smoke detector principal, we can now appreciate that not every common threat needs full armored protection. The signal detection theory in this paper shows where a person draws line when they overestimate or underestimate anxiety.
It talks about “optimal threshold” to show a threat response in given situation. Optimal threshold is a mathematical parameter which is function of probability of the occurrence real event and vulnerability of the individual.
The signal detection theory says that the superposition of response signals for given background noise and response signal from real threat give us the quantified judgement of how intensely the anxiety is triggered compared to the practicality of the threat – this quantified judgement is called optimal threshold (λ). Lower the threshold more intensely the anxiety will be triggered for given disturbance – background noise.

Figure 1 : Signal detection problem, how the optimal threshold can be calculated. (Credit: Anxiety: An Evolutionary Approach, 2011, Bateson et al., Canadian Journal of Psychiatry)

Equation 1: optimum threshold (Credit: Anxiety: An Evolutionary Approach, 2011, Bateson et al.,Canadian Journal of Psychiatry)
Here,
λ = optimal threshold
pnt= probability that there is no threat
pt= probability that there is real threat
wfa= cost of false alarm
wmiss = cost of a miss
Once this equation comes in focus the discussion becomes interesting. The ratio of pnt to pt mathematically quantifies how practical the threat is. The ratio of wfa to wmiss mathematically quantifies what will be the cost if the anxiety trigger is accepted or rejected – will the subject live or die. This ratio shows how we trigger anxiety response. If the cost of responding is nothing for even a simple threat scenario, we will choose to trigger that response, same would happen if the cost of losing is ultimately the loss of life, we would trigger any possible anxiety response to avoid it. The authors call this ratio as individual’s vulnerability.
The ratio (pnt/pt) can be seen like this. If the surrounding really is hostile and consists of events which cause many life altering events than the safety ensuring events then the pt (probability of threat) will be way higher than pnt (probability of no threat and safer environment). In war situation where multiple bombings, gun firings are happening around you the probability of threat happening (pt) is way high than it not happening (pnt). The optimal threshold will drop immediately and anxiety triggered will be very high.
The ratio (wfa / wmiss) can be seen like this. If the person is way stronger to handle given threat, then the person will need no effort, investment or cost to trigger any reaction alarm to even a false threat. Consider the example where you are about to be bit by mosquito, you know the efforts to slap many times until the mosquito dies are not worthless, you will try many times to kill it even when you know it will swiftly escape, you are less vulnerable in this scenario. But now when you are about to be killed by John Wick (!?) you know for sure that even a pencil will do the job for him, any environment is hostile for you, you are vulnerable here, the value of losing life (wmiss)is way high than the cost of attempts to save it (wfa). Your optimal threshold will immediately drop down thus triggering intense anxiety.
Once you generate enough data for such optimal frequencies you can easily distinguish the healthy anxiety responses and anxiety disorders. I loved how these two factors (probability of threat and vulnerability of an individual) can predict the levels of anxiety in a person. This equation explains and can also quantify why pregnant women have heightened awareness of their surroundings, why people get insomniac after constant mental stress, why restless people are always in the mode of action and fight, why reclusive people hesitate to visit foreign, unknown places.
Your Surroundings and Mindset Matter!
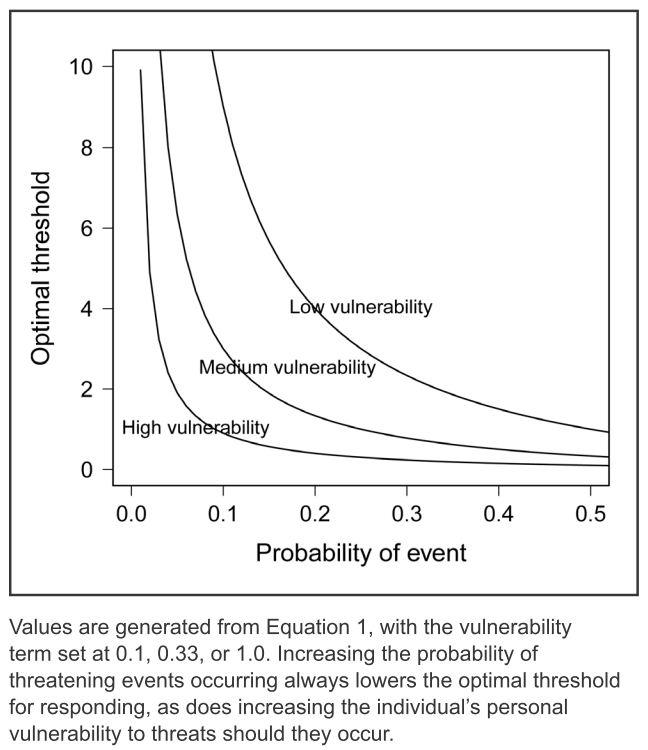
Figure 2 : Three levels of vulnerability, here optimal threshold and probability of event can be correlated for difference in the anxiety responses (Credit: Anxiety: An Evolutionary Approach, 2011, Bateson et al., Canadian Journal of Psychiatry)
It is really interesting what the authors have achieved and established in this research. They compared three different levels of vulnerability and explained them using given plot. The thing to highlight here for anxiety disorders is that they emerge from the environments which always keep on presenting high probabilistic practically threatening scenarios. The anxiety disorders also emerge when the individual feels more vulnerable.
Higher the vulnerability lower will be the optimal threshold and intense will be the anxiety response.
As shown in research, in the uncertain times of Covid-19 people who were locked in their home had no disorders, were not exposed to the virus also felt anxious and faced some anxiety disorders because of the environment they were in.
If the person feels less vulnerable and stronger then even for given strong life-threatening events the optimal threshold will be higher thus the anxiety triggered will be lower.

Are you noticing where this is going?
This is a mathematical model which shows how a healthy, supportive, and safe environment and also a strong mindset and better judgment of reality is important for handling challenging situations.
For a person suffering from anxiety disorder, it becomes very important to make sure that they know that they are in a safer environment and are cared for. It is very important to make them feel safe and understood. Creating a system of critical thinking and reasoning can also help the person to have a sense of strength and high resistance to vulnerability, this also goes for physical strength. The vulnerability is not only mental it is also physical when it comes to reality.
You will now appreciate why teenagers and trauma patients are more exposed to anxiety disorders. Mostly and generally in teenagers it is due to the uncertainty of many new things happening with them simultaneously and in trauma patients it’s the constant bombardment of life-threatening events in hostile environments.

Conclusion
Anxiety serves to prepare a person for threats. The emotion called anxiety is an evolutionary gift to ensure long survival of our species but as it is also related to our primitive instincts, we mostly let anxiety overpower other emotions in seemingly safer scenarios. Strategy and anticipation are the gifts of anxiety but if overused they will end up in imparting unnecessary caution and overprotective attitude which inhibits adaptation to changes there by slowing evolution of our species. Anxiety just like pain is one uncomfortable but effective way to cope up with the adversities in life, that’s how we build strength, resistance and deeper understanding of the surrounding for better and more precisely predictable future.
The remarkable concepts like smoke detector principal and optimal threshold in signal detection theory developed by modern psychologists/ psychiatrists help us to draw a line between a healthy anxiety (adaptive function) and unhealthy anxiety (pathology) and ways to handle/ treat them effectively.
These theories show how we can quantify seemingly intangible emotions like anxiety and way to handle them. If you can measure something effectively you can control and predict it effectively. All credit goes to such brilliant minds!
References, Image sources and further reading:
- Fear of the unknown: One fear to rule them all?, 2016, R. Nicholas Carleton, Journal of Anxiety Disorders
- Natural selection and the regulation of defenses: A signal detection analysis of the smoke detector principle, 2005, Randolph M. Nesse,Evolution and Human Behavior
- Natural Selection and the Regulation of Defensive Responses, ANNALS NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES, Randolph M. Nesse
- Anxiety: An Evolutionary Approach, 2011, Bateson et al., Canadian Journal of Psychiatry
- The relationship between perceived stress and emotional distress during the COVID-19 outbreak: Effects of boredom proneness and coping style, 2021, Yan et al., Journal of Anxiety Disorders
- Long-term effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy for youth with anxiety disorders, 2018, Kodal et al., Journal of Anxiety Disorders
- Anxiety, National Library of Medicine, www.medlineplus.gov
- Anxiety Disorders, National Institute of Mental Health
- What are Anxiety Disorders?, American Psychiatric Association
- Anxiety – Wikipedia
- Randolph M. Nesse, M.D., Professor Emeritus of Psychiatry, Professor Emeritus of Psychology, Department of Psychiatry, University of Michigan
- Everything You Need to Know About Anxiety – www.healthline.com