Neuroscience of the languages of love

Background – What is love? What is an emotion?
Emotions are one inseparable part of human life rather every living thing. They can be attributed as the response we generate for the interactions we have with our surrounding – a response to various stimuli. Responding to the events/ interactions is one important way of communication for living things. Out of these responses, physical responses are generally very easy to notice and interpret but at the same time the emotional responses are more complicated, sometimes difficult to even notice and interpret. Body language mostly gives away the what’s going in a person’s head, what they are thinking (like most of us have a tell when we are uncomfortable/ nervous or are lying). Understanding body language can give straightforward answers about person’s condition and personality but it is always difficult to gauge what exactly the person is feeling in given condition.
Love is one of the most important and at the same time the most exploited feelings we living things have. Love is the feeling which we can connect with anything real and imaginary that is there in the universe (trust me, this is not inferred from the pop culture philosophy) There are more things to love than to hate for everyone of us. For the sake of generalization, love brings in the comfort, safety and hope for the survival of every species. Love for certain things can push the individual to do something extraordinary – good (because it can create purpose irrespective of the situations and challenges in life) or bad (that is exactly why love is the most exploited emotion, you can make people do wrong things just for the sake of love).
Love language
Even though love is the most general emotion all of us have (like love for something, some person, some song, some place, some season, some animal, love for everything); the love between couples – romantic couples remain always at the focal point. The love between couples is not important because pop culture, poets, painters, singers, saints mentioned it repeatedly everywhere; it is important because it is what makes our lives less artificial. The love romantic couple can have, affects the future of society in every possible and productive way – it also ensures diversity – randomness in species. As we are highly expressive and responsive species, communication is the most important part of our life especially the love life. When two people from different backgrounds come together in the name of love it becomes very important as how they express their love for each other. Today we call it “the love language”. Some couples love to talk a lot with each other, some like to sit in silence together, some always feel cuddly, some would be always staring into each other’s eyes, some would travel together, some like to cook together or for other, some like to eat together, some are always pulling pranks, some would peel orange for the others, some would send flowers, some would be writing poems, singing songs, some would always fight (yes…, you read that and accepted it). You get it; every couple has their own (sometimes weird) love language and communicating in this certain language deepens the relationship.
Brain vs heart – Neuroscience of love
Even though heart has been attributed to the origin of the feeling of love due to various reason, its original job is to just pump the blood. Nothing interesting happens in the heart of a person in love than in their brain. Brain surely is the epicenter for the study of love and how we feel when we are in love. Just like love, our brain is the most complicated thing we are yet to understand fully. Neuroscientists are always trying to figure out what generates certain set of emotions and responses. Love is one such important emotion which is also an attractive subject for them. Its association with every aspect of our life, its complexity and simplicity at the same time has always attracted scientists who are trying to understand human behavior. (love hasn’t spared the brainiacs too.)
Modern neuroscience is blurring the lines between the intangibility of emotions especially love and the tangible – physical parameters like electricity (synapse, wave-forms), chemicals (hormones, neurotransmitters). From providing shock to certain part of the brain to see which muscle it twitches to enabling the paralyzed people to walk again through brain implants, neuroscience has had many quantum leaps.

How does a neuroscientist interpret love?
I think every person who is in love can tell what it is but it will always have a touch of subjectivity, thus a neuroscientist is always the most qualified person to create an objective fact on the emotion of love.
Today we will see an interesting study in neuroscience about the emotions in romantic couples. Before going into the details and the conclusions of the study, it is important to roughly get the hold of some concepts neuroscientists used to interpret their results.
Our brain is made of approximately 100 billion neurons whose network is always firing some electrical signals to generate responses and create memories. The measurement of such electrical signals and their interpretation is important aspect of studying brain.
fMRI – functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
It is found that when there is a neural activation in brain, the blood flow increases in that region. This change in blood flow can be monitored using functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
De-oxygenated hemoglobin in blood is paramagnetic (attracted by external magnetic field) and oxygenated hemoglobin in blood is diamagnetic (repelled by external magnetic field). Producing a strong magnetic field around brain and monitoring their interactions with the magnetic fields generated during blood flow are measured in MRI. Such measurements require bulky and specialized instruments with controlled conditions.
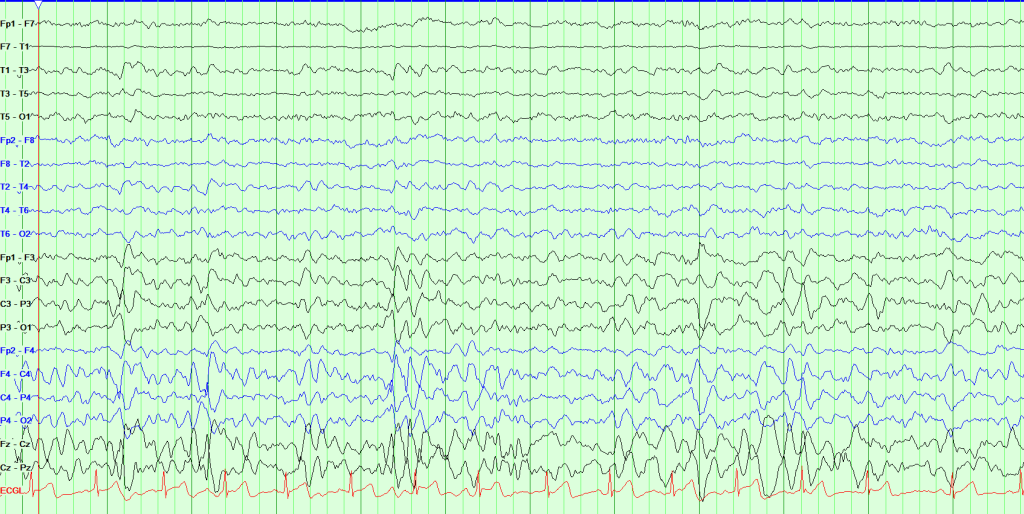
Electroencephalography (EEG) – it is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. It monitors the electrical signals from brain using electrodes on scalp instead of measuring the changes in magnetic fields. The EEG devices are now very lightweight and portable thus they have less influence on the neural activity of the subject under observation. The portability also widens the test environments for the subjects under observation.
EEG can be used to interpret the signals from the outer surface (cerebral cortex) of the brain as the electrodes are put on the scalp. It is difficult to understand what is happening inside the brain from the signals of EEG although they will always be interfering with the overall signals sensed by the electrode at the scalp.

International 10-20 system – It is an internationally accepted template for putting electrodes proportionately on the scalp of head. This ensures homogeneous observations and reproducibility of the results during EEG. 10 and 20 refer to the percentage of the gap between the electrodes meaning the electrodes are placed at 10% or 20% of the total distance between front – back of the skull (called as nasion and inion respectively) or total left-right distance.
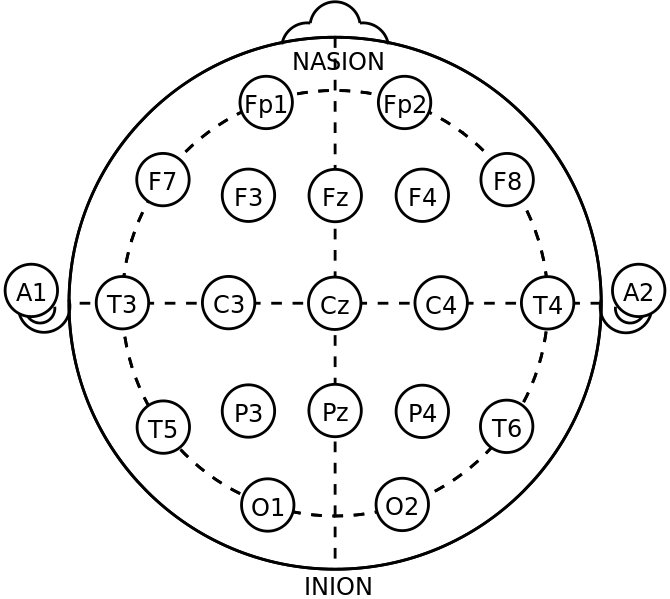
A good, healthy person will show waves of certain frequencies according to their conditions. These frequencies are between 1 to 30 Hz and the amplitude varies between 20 to 100 micro volt. The frequencies are divided as follows:
Alpha waves – alpha waves have frequency between 8-12 Hz and are observed when a person is relaxed in a wakeful condition. These are mainly attributed to activity in parietal and occipital lobe of the brain. When a relaxed person opens their eyes, it is observed that their alpha activity reduces and beta activity increases. Alpha waves are produced when you’re awake but your mind is in a resting state.
Beta waves – beta waves have frequency above 12 till 30 Hz. Beta waves are associated with intense mental activity like doing some arithmetic calculations, making inferences from given data, being busy, focused on something. The frontal area of brain shows significant beta activity in such wakeful instances.
Gamma waves – these are the fastest brain waves with frequency between 30-80 Hz. They are attributed to deep thinking and state of high focus. Generally, people with high IQ show more gamma activity; lower gamma activity is attributed to memory and learning problems, short attention span.
Delta waves – delta waves are associated with frequencies between 0.5 – 4 Hz
Theta waves – theta waves are associated with frequencies between 4-7 Hz
Theta and delta waves are not observed in wakeful state. If delta and theta waves are observed in wakefulness then it indicates brain dysfunction.
Lateralization of brain – We have come across one misleading fact that we only use certain fraction/ percentage of our brain in routine activities. (the popular number is 5-20%) This popular but wrong fact could be attributed to the idea of lateralization of brain. (Sci-Fi movies have exploited this wrong fact already)
Generally, almost all areas of every healthy person’s brain are always active. But, certain cognitive functions or neural functions (like movement of body parts, thinking, calculating, watching, tasting) are associated to either of the hemisphere of the brain (left or right hemisphere). Although brain as a whole is always active, certain activities/ functions activate one hemisphere more that the another one. Simply put, there is difference in brain signals between right and left hemisphere during a cognitive function. This dominance of brain signal from one “side” shows lateralization of brain. One side will be more activated in brain for given activity.
Asymmetry indices (AI) – So, this heightened activity from one side of brain is measured by taking difference of the signal power of the brain waves from left and right hemisphere.
Increased asymmetry index indicates that the signals in right hemisphere are getting inhibited, restricted. Thus, left hemisphere especially left frontal activity in brain is increased.
Decreased asymmetry index means that the signals in left hemisphere are getting inhibited and thereby right hemisphere is more activated.
Simply put, more the asymmetry index more is the activity in left part of the brain.
There are two main theories on how our brain is lateralized. One is Valence Model (VM) and another is Right Hemisphere Hypothesis (RHH).
VM – According to valence model, every emotion has a valence meaning a tendency to be preferable – positive and rewarding or not preferable – negative and aversion inducing. The positive, rewarding emotions are processed in left hemisphere and negative, punishing emotions are processed in right hemisphere of the brain.
RHH – Right Hemispherical Hypothesis says that whatever may the emotions be – positive or negative, rewarding or punishing – all are processed in right hemisphere of the brain.
Neuroscientists are yet to reach a consensus on which of these two ideas are right. Certain observations are supported by VM and others are supported by RHH. It’s not about what is wrong and what is right, it is about which model explains given dataset better and predicts better.
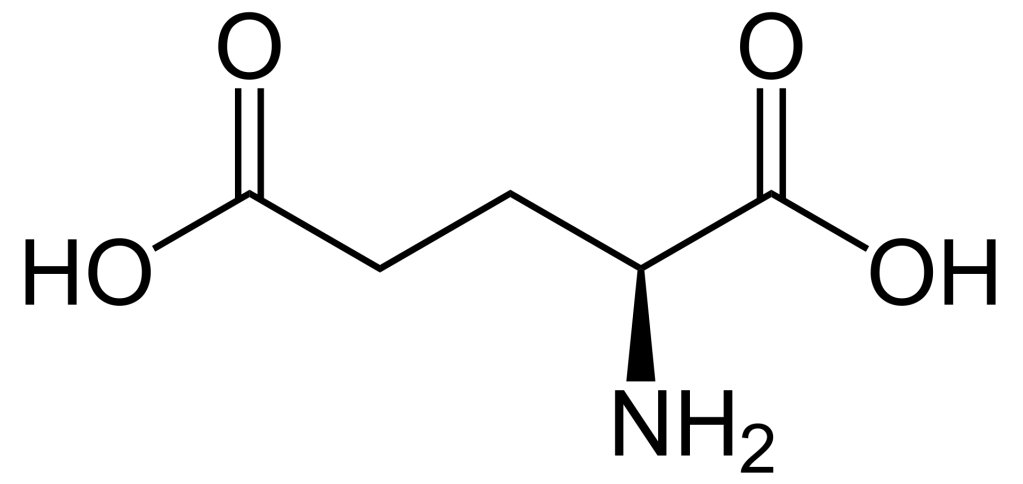
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) – this is one of the chemicals – a neurotransmitter which inhibits/ blocks certain neural signals thereby is responsible for creating calmness. If GABA is released more, we feel calmer and more relaxed. The opposite effect i.e. restlessness, excitement is generated by glutamate. For a healthy brain balance between GABA and Glutamate is important.
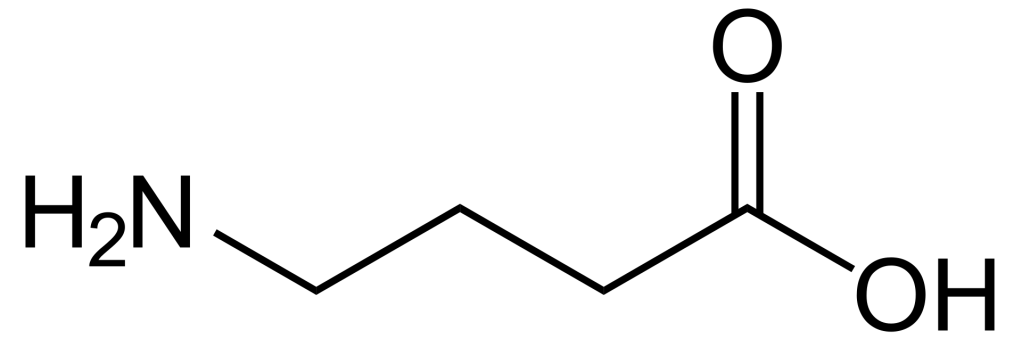
Glutamate is the main excitatory and GABA the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian cortex. The prescription drugs for reducing restlessness/ improving calmness ensure high levels of GABA in our central nervous system.
Now that we have understood certain basic ideas to understand the experiment, let us see how certain languages of love in romantic couples affect their neural responses.
The Experiment
The neuroscientists studied three conditions in romantic couples namely – speech, hug and kiss.
The participating romantic partners were asked to wear the EEG system to record the brain signal during the experiment. Scientists recorded a baseline – a neutral state for speech, hug and kiss. Then the emotional states were recorded through certain assigned tasks.
In neutral state for speech, one of the partners listened to a generic weather report, whereas in the emotional state for speech the partner listened to a recording of their partner reading an emotional shared life experience.
In neutral state for hugging/ embracing the partner hugged a pillow while the another being absent and in emotional embrace, they hugged each other.
In neutral state for kissing one partner kissed their hand and in emotional state the partners kissed each other.
Why this experimental setup is important?
According to the authors of this paper, most of the studies to understand the brain activities are always performed in controlled setup which conditions the brain signals in a set template. The observations may create certain insights but are less close to the reality as they were not observed in real life conditions. Authors claim that this method to actually measure the brain signals in real life scenarios creates more relevant, closer to real life dataset. The responses in such setup are more natural. That is why they claim this experiment having more “ecological validity”
The authors make a great attempt to understand the main and most preferred language of love in romantic couples i.e., kissing, embracing, speaking shared experiences. It will be really interesting to see what “flashes” we have when we are experiencing such events.
Observations – looking from a neuroscientist’s perspective
Following are the key observations authors present in this paper:
- Participants were more positive after executing the behavioral tasks.
- Brain gets lateralized during emotional processing.
- High asymmetry index in front lobe electrodes was found during emotional kissing compared to neutral kissing. Researchers found high alpha AI during emotional (real/ organic) kissing than neutral (artificial) kissing baseline.
- Found lower alpha AI during speech.
- Higher AI in kissing and emotional speech.
- Researchers didn’t find overall effects in alpha or beta for embracing. Only males showed higher beta AI in the embracing condition.
Conclusions
Pardon my oversimplification for the sake of understanding.
- The first observation is the easiest to understand. Kissing, hugging, and telling a shared memory/ experience of love surely makes the romance to flourish more (duh!)
- The lateralization of brain means that certain emotions are flagged in one of the hemispheres of the brain. It’s not like all the emotions activate only one side of the brain.
- This one is interesting. High alpha asymmetry index during kissing means that left brain is more activated during kissing. The authors put forward that this is related to release of GABA molecules in right hemisphere which inhibit the neural signals thereby create a calming effect. Valence model says that left hemisphere processes positive and rewarding emotions. So, this observation shows that kissing surely creates a positive effect in the brain of the romantic couples. Higher left hemispherical activity is attributed to more positivity in a study. It is important observation of high alpha asymmetry because its opposite i.e., lower alpha activity is linked with suicidal tendencies in depression as observed in a study.
- The authors found that the VM theory holds best to explain events in frontal part of the brain whereas the RHH theory can explain the posterior events in brain. That is exactly why low alpha AI in romantic/ emotional speech cannot be directly correlated negative emotions which the Valence Model says. Rather according to the RHH theory the speech invokes strong right hemispherical activity. The authors found an observation to link VM and RHH theories according to the regions of brain considered for discussion. Both theories are not completely wrong but are successful when implemented to specific region of the brain. Simply put, it is not just about preference to left or right hemisphere – it is also about whether the activity is in front or back portion of the brain.
- High asymmetry indices during kissing and emotional speech show how strongly they affect the lovers. Emotional speech is as effective as kissing. (it’s like kissing your lover’s brain with your emotional words!)
- This one is also one more interesting observation. As there are no significant effects in alpha or beta asymmetries during hugging activity, it means the hugging is less effective than kissing or emotional speech. But the authors present a catch here! They found a sex specific observation. It says, high beta AI in males during embracing. High beta AI is linked with increased emotional, cognitive processing. This means that men consider hugging more emotional than women. Women process hugging as a casual act but men consider it more thoughtful especially when they are hugging the existing and well-familiar female partner. Authors attribute this to the fact that women generally hug each other (female-female hug) more than men do (male-male hug).
What does this mean to common person?
The experiment authors performed was really interesting and was closer to the real-life conditions. If you want more interesting details on how what and why the experiment was designed in a certain way and how the results were interpreted, I have provided the link at the end. Going through this article puts front some really deep insights on how love, romance affects our brain. How these languages to express love create a deep connection between lovers.
The authors have tried to remain as objective as possible. But, again pardon my oversimplification, here is what one can understand from this experiment:
Having emotional discussions with your partner is as effective as kissing your partner. No wonder people resort to poetry, music, and literature to express their love. The more you are able to express your love for your partner the more positively it is going to influence your brain thereby you. You also feel better for yourself if you can express your love to your partner. It is like the act loving your partner is providing strength to yourself. Maybe this is how lovers become strong mentally. (No wonder couples madly in love are ready to fight the whole world!) Kissing your romantic partner has calming effect on you mental state. (I think almost no one needs explanation on that! But don’t forget that speech is equally potent)
And finally, men need more hugs compared to women! Although hugging is a common act in society, men are highly emotional when it comes to hugging. So, this is an advice not only for women but also for men and especially for men that you hug your bro, your buddy whenever you feel like expressing your love for them.
Our brain being one of the least understood wonders of the universe has always tricked us in spite of being the most vital part of our existence. The insights from such experiments in neuroscience with this closeness to reality bring more clarity in the ways we handle our relationships. We definitely owe thanks to the authors/ researchers involved in such studies for their valuable insights.

Reference article –
- Investigating real-life emotions in romantic couples: a mobile EEG study – Packheiser, J., Berretz, G., Rook, N. et al.
Further reading –
- Frontal Alpha Asymmetry and Negative Mood: A Cross-Sectional Study in Older and Younger Adults -Barros, C.; Pereira, A.R.; Sampaio, A.; Buján, A.; Pinal, D.
- Frontal Alpha Asymmetry Correlates with Suicidal Behavior in Major Depressive Disorder – Park Y, Jung W, Kim S, Jeon H, Lee SH.