Why the philosophical search for the ultimate universal truth is useless?
An Existential Meme Caption and Its Resolution
Since the invention of social media, some images (especially the certain classic meme templates) have stood the test of time. These images keep on circulating and there comes a moment when that image reinvents itself in new format, it brings some new argument with different type of humor. See the following image for example:
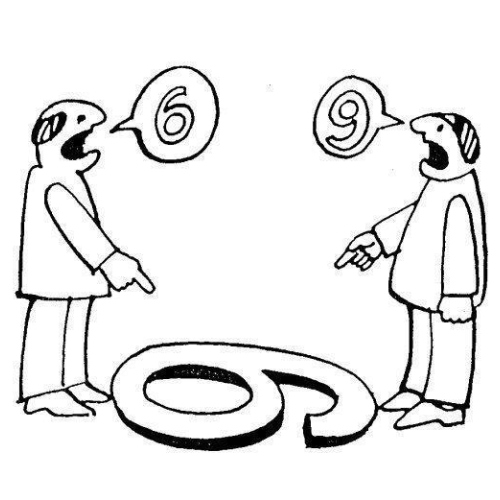
Funnily enough, this image always comes with a thoughtful (supposedly) caption as follows:
“Just because you are right, does not mean, I am wrong. You just haven’t seen life from my side”
Given that the argument presented in this caption demonstrates the subjectivity of the everyone’s perspective, it is really futile to discuss what to exactly extract or understand from this caption.
For example, if this was the scenario where knowing the true value would save a person’s life then knowing the truth becomes the necessity and all of us know that this wouldn’t have saved that precious life which was dependent the true answer. There is no definite answer for this argument because it invokes subjectivity in the argument. People use this image and the said caption to express their inability to prove the truth value of their argument, especially their emotions.
Now, in recent time this image resurfaced with a new argument which blew my mind the moment I saw it. The reinvented image looks like this:
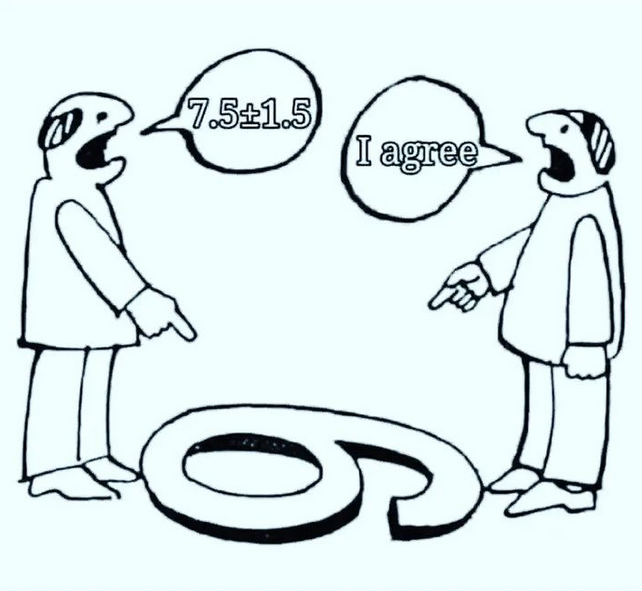
You must appreciate wit and sense of humor of the person who modified the argument presented in the original image.
There Is No Final Truth.
This simple evolution of a very common internet template invites a question. What is the real truth? What is the truest truth? What is that one answer that can answer all the questions? If something exists in truth, then how would I verify that it is “the truth”?
At first one might think that these are such foolish questions. Truth can be established by experimentation, demonstration, repeatability/ reproducibility, comparison, consistency, contradiction/ counterexamples.
Take for example,
Q1: how would one calculate the time taken by the ball dropped from certain height on the Earth to reach the ground?
A1: The answer is by using Newton’s kinematic equations.
Q2: How the kinematic equations were developed?
A2: By using Newton’s law of gravitation and the law of motion
Q3: How these laws were developed?
A3: Newton studied the motion of moon and earth, developed some mathematics to explain that behavior. That math remains consistent to explain the scenario of the motion of the ball dropped from certain height.
Now from here the real fun begins,
Q4: If Newton’s law of gravitation and laws of motion are consistent and hence true then why did they fail to explain the different/anomalous motion of the planet Mercury around the Sun?
A4: The truth presented in Newton’s laws of gravitation and motions are a special case of the higher and more inclusive, exhaustive truth of Einstein’s relativity.
Q5: Why Newton’s truth is not the complete/ ultimate truth?
A5: Newton assumed Gravitational as a universal force of attraction, inertia of every object in the universe, concepts of the balanced force.
Q6: Did Newton made mistake in “assuming” certain things for the sake of establishing the proof and its mathematics? Because, Einstein certainly didn’t assume those things and still his theory of relativity can prove the arguments covered by Newton.
A6: Yes, looks like Newton assumed gravity as a force of attraction where things will get “pulled” towards heavier objects or fall into them. Whereas Einstein established this as wrong and proved that Gravity is actually a “push” created due the curvature in space-time.
Now from hereon, if one remains careful enough then that person can land into the territory of quantum mechanics to prove that Einstein was wrong (in a way). The failure that connect the Theory of relativity and quantum mechanics is why we are still uncertain what is the ultimate truth that will answer all the questions there exist. (Trust me the answer is definitely not “42”!)
So, if we keep on asking the question to each and every truth, will we reach the ultimate truth? Will that be the ultimate knowledge? Will that help us define the absoluteness of the knowledge?
Philosophers have argued (literally and figuratively) for centuries about the acceptability of any truth as “the truth”. Epistemology deals with the theory of knowledge, how a belief and opinion differ from the truth, if given argument is true then how it becomes the truth- what is its validity, justification?
So, when one starts to question things continuously there will be three possible cases explaining how the things will end into. This condition is famously known as Agrippa’s Trilemma or the Münchhausen trilemma in philosophy.
In really simple words, the trilemma says that it is impossible to prove whether certain truth is really true because at the last end of this truth there will always be some unjustified, non-contradictory fact which cannot be proved by using other proofs in existence.
Let see in detail what is this trilemma and the its legacy in epistemology.
The Münchhausen Trilemma
Baron Münchhausen is a fictional character created by German writer Rudolf Erich Raspe in his book “Baron Munchausen’s Narrative of his Marvelous Travels and Campaigns in Russia”. Münchhausen is a person who has done many impossible things like fighting a forty-foot crocodile, and traveling to the Moon. The book is a satire. (Baron Münchhausen is German Don Quixote per say!)
So, there is a story where Baron Münchhausen is drowning in the water while riding on his horse but soon he realizes that he can lift himself from the water just by pulling his hair. Hence, he pulls his hair and comes out of that mire/ quicksand with his horse.
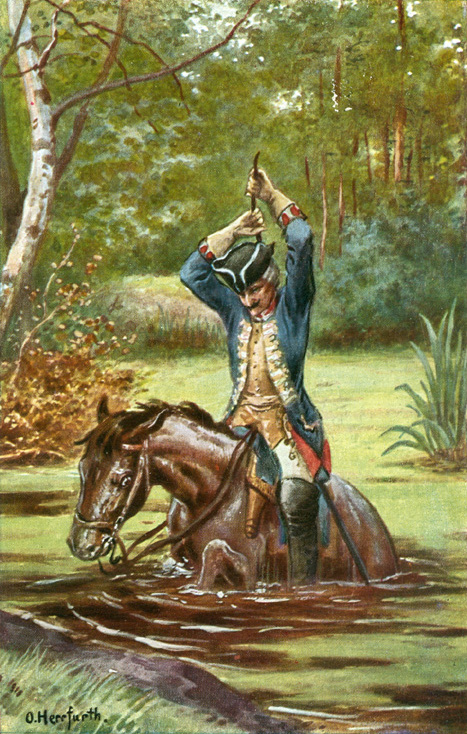

Do you understand how it worked? How could one pull himself out of an unsupported marshy land without any support? Where did Münchhausen pivot to rest himself? The story is foolish!
So, how did Münchhausen come out of mire without any support? If he was successful in his rescue, he would have definitely used some pivot, some support!
In the similar emotion, any argument to be proven true will need another supporting true argument. This “primary supporting true argument” will also need another “secondary supporting true argument”. You might have understood where we are going with this. If this keeps on progressing further and we keep questioning the complementary true arguments which are supporting the main truth then we will end up in three possible scenarios, which are “the trilemmas” as follows:
If we keep on questioning anything, the proofs will:
- Given proof will be followed by other distinct proofs which further will be proved by other more distinct proofs leading to infinite chain of proofs – The regressive argument
- A proof will be proved by another proof based on the prejudice that it is consistent in many cases so, as it is consistent then it must be true hence the main proof is true – The circular argument
- The proof will be accepted as the truth as there is no proven counterargument or any contradicting observation to falsify it – The dogmatic argument
Resolving the Trilemma
Explaining these trilemmas, we can say that these three trilemmas can be solved by following ways:
- Infinitism: there will be an infinite chain of justifications for every truth. It will never end.
Remember that child who annoys their parents with a new question to every answer they give. That child indirectly knows infinite reasoning! (somehow!) A “patient” parent can go on answering that child’s each and every question!
- Coherentism: there will be recurring loop of beliefs based on some other beliefs. These beliefs will prove each other.
You know your friend is telling you the truth because you have always seen him/her telling you the truth. It is consistent with his behavior. As you “believe” that he/ she tells the truth, whatever is told by them would also be true. (But who knows!)
- Foundationalism: the chain of justifications will end at an argument which is accepted as the truth without any other proof and/or because there is no contraction available to this argument. It becomes accepted as an axiom which lies at the foundation of everything.
The matter was accepted to be made up of smallest invisible particle called atom and based on that many good theories explaining reaction stoichiometry, formation of molecules and thereby compounds was explained. We now know that atom can constitute further divisible particles thereby upgrading the theory further on to cover more generalized cases till quantum systems.
Similarly, Newton’s ideas which we discussed in the start rested on some foundation which proved many truths based on that foundation. It was the failure of that foundation which could not explain the motion of mercury. Einstein’s new foundation embraced wider foundation where Newton’s math becomes a special case. We will keep on upgrading our foundations.
Skepticism, Agrippa and the Suspension of the Judgement
There was a school of Greek philosophers who questioned the very existence of the knowledge. They were “skeptical”, “doubtful” about everything thereby forming the school of Skepticism in philosophy. The reason to question everything available around us was due to the ways through which we understand these things. There is a gap between how we experience things around us through our senses and what these things really are. (What we see in desert looking like a lake is actually a mirage) There will always be some gap between appearance and reality. So, what we are believing to be true does not necessarily requires to remain true. The reality might be totally different. Not only different but reality can be subjective meaning that what a person has experienced from a thing can be totally different from what another person has experienced, and both stand true because of the individuality of their ways of experiencing the reality. Both sides will be true due to distinct and unprovable subjectivity. Bertrand Russel in his book the Problems of Philosophy has clearly discussed this as the limitations of our senses and the nature of reality. these limitations of our senses bring in that subjectivity in our truths hence they are our versions of truths which may be the truths for others. So, the early idea was to question everything to suspend both beliefs, experiences or the versions of the truth.
The problem which is created here is that if people become doubtful about everything around them, then they will end up in questioning their own existence. This question of existence will further lead to infinite chain thereby rendering useless, worthless, and futile venture. That is exactly why Socrates pursued ethics where “Why to live?” is not that much important and where “How to live?” is much more important.
One of the important philosophers called Pyrrho ((360-270 BCE) traveled with the army of Alexander to India where he met some “naked philosophers” (gymnosophists) who explained to him the reality of life. That there is no such thing as true or false, nothing is just or unjust, neither is honorable or dishonorable. No belief or experience is true or false. From these naked philosophers (I think these were the ancient groups of “Naga Sadhus” which exist even in our time today). These learnings focus on not having any judgement thereby rejecting any judgement, suspending any judgement.
This gave rise to the formation of five tropes for suspension of judgement which were developed by Agrippa who came later and expanded the understandings of Pyrrho.
These five tropes go like this:
- When the views are conflicting between common people and the philosophers then we must suspend that judgement – unacceptable due to inconsistency – Dissent
- When one is justifying a claim then that claim must be appealed by a prior claim which will end in infinite regress, so we must suspend that judgement – Progress ad infinitum
- Everything is relative, things appear right or wrong based on the condition in which they were observed and the environments in which they were judged, so we must suspend that judgement – Relation
- When a judgment is proved to be true based on an assumption and if that assumption itself is unsupported then we must suspend that judgement – Assumption
- When a truth invokes another proof which creates the circularity of justifications then we must suspend that judgement – Circularity
The beauty of the Agrippa’s five tropes is that it brings in the relativity in our process of understanding the truths of our lives. I would say that Agrippa solved the problem of establishing the truth by the process of elimination. In a very smart way, instead of proving something directly to be true, we can work around the facts surrounding given argument. Eliminating the arguments in the proof by implementing these five tropes can at least reduce the size of the problem thereby keeping all the possibilities of proving it to be true always open. The beauty is in the opportunities to upgrade the foundations!
This philosophy of skepticism created the foundation of modern philosophy and thereby modern science and mathematics. Some ideas explained in this trilemma remain consistent with the Kurt Gödel’s Incompleteness Theorem which explains why mathematics rather the reality itself is inconsistent. There will always be something unprovable in given domain of system which will demand to expand that system to a totally new system of knowledge thereby upgrading the existing foundations of our understanding of the nature and the reality and thereby our fields knowledge. That is exactly why Newton’s ideas even though were limited to some special cases are important because Einstein wouldn’t have had the foundation to build upon something. We will always be creating some general understanding of the universe which later will surely become a special case in our understanding. That is also why questioning everything is important in the process of developing fundamental understanding. It is the philosophy of skepticism which empowers us to stay humble and rediscover the reality in which we already exist.