Rudyard Kipling is famously known for the creation of ‘The Jungle Book’. He is the youngest British Nobel Laureate (at the age of 41) till date.

Today we will be deep diving into Rudyard Kipling’s all time famous and many people’s favorite poem ‘If-‘. This poem written in 1895 was published in his famous historical fantasy book called ‘Rewards and Fairies’ in 1910.
This poem is all about a set of recommendations from poet to the reader (or his son) to become a person of greater values, virtues in order to handle every situation in life irrespective of its outcomes. The only motivation to act on something must be our intent of welfare of ourselves and the society around us as a human being and only thing we can control is our perception of things is the core idea of this poem.
If you can keep your head when all about you
Are losing theirs and blaming it on you;
If you can trust yourself when all men doubt you,
But make allowance for their doubting too:
This is about believing in ourselves and freeing ourselves from self-doubt. It is also about remaining content when everyone is against you. It focused on not losing sanity when everything around you seems to have lost the meaning, when everyone behaves like they have lost their minds, when chaos has surrounded you. This is the time which will demand you to remain confident of your intentions.
If you can wait and not be tired by waiting,
Or being lied about, don’t deal in lies,
Or being hated, don’t give way to hating,
And yet don’t look too good, nor talk too wise;
This is more about remaining calm, balanced and unaffected. There might be several times where the results won’t be immediate, one should deal it with patience. It is about the moving away from instant gratification and not doing things for immediate pleasures. Especially, in the times of Social-media instant gratification has become a very innate thing in the human behavior.
When you will be lied to or when you will be hated, a person’s behavior must not favor the idea of ‘tit for tat’ or ‘an eye for an eye’ indicating reactive behavior, retaliating behavior. Rather not dealing in lies, abiding to the truth even when lied to and not hating even when hated are the virtues poet wishes to have in the reader. The balanced behavior of humility in smart person and simplicity in good looking person will make him a desirable person. Otherwise, who values a smart but arrogant person anyways!
If you can dream—and not make dreams your master;
If you can think—and not make thoughts your aim,
If you can meet with Triumph and Disaster
And treat those two impostors just the same:
This is about the what you do with your life and how you do it. It is about finding the purpose of your being in the life and envisioning yourself to fulfill that purpose. You should not be consumed by the dreams solely- thereby causing in-actions; the poet expects the reader to have actions for achieving these dreams and visions. Winning and losing are called imposters here because of the nature of our perception about them; one is desirable and the another one is not. The mere possibility of loss leads to inaction causes us to go deeper into the negative feeling of not achieving anything. The poet wants reader to not care about the consequences which are not in the hands of doer rather do the immediate things to get the consequences (whatever they may) which are always in the hands of doer.
The best way to come out of indecision is to act on things which are in our immediate control.
If you can bear to hear the truth you’ve spoken
Twisted by knaves to make a trap for fools,
Or watch the things you gave your life to, broken,
And stoop and build ’em up with worn-out tools;
This is about remaining committed and honest to your words, keeping your promises. This will demand a person to face the truth, make others aware of the truth when they are being fooled by some dishonest people and this requires courage. It is about remaining committed to the purpose even when things will fall down and you will feel that the virtues you are living with have worn-out and are of no value as they didn’t yield immediate favorable effects. This is some sort of test that you should go through to reach your ultimate pure desires.
If you can make one heap of all your winnings
And risk it on one turn of pitch-and-toss,
And lose, and start again at your beginnings
And never breathe a word about your loss;
If you can force your heart and nerve and sinew
To serve your turn long after they are gone,
And so hold on when there is nothing in you
Except the Will which says to them: ‘Hold on!’
Here, our poet wants the reader to have a really great goal in life whose purpose must be to leave an example or a legacy for others to follow as a light house. The greatness of this purpose will make him to sacrifice any great achievement, great possession for the greatness of purpose is the only thing that will not perish. All the great possessions or the biggest of big losses are valueless in front of a great purpose or a great legacy. These can be the sacrifices in the great journey.
The loss of hard earned possessions, achievements may force a person to lose his interest in the journey; but the person’s resilience and the will to hold on to the greater purpose will define what is inside him, what he is made of !
If you can talk with crowds and keep your virtue,
Or walk with Kings—nor lose the common touch,
If neither foes nor loving friends can hurt you,
If all men count with you, but none too much:
The poet talks here about doing what you are saying, being aware of the reality and being humble and dependable yet remain unaffected by too much expectations of people around you- friends or enemies. It is about not getting flattered by the good opinions from the people loving you and not getting despised of the bad opinions of your haters or enemies. It is about being free from the opinions, projections of the people around you.
If you can fill the unforgiving minute
With sixty seconds’ worth of distance run,
Unforgiving nature of time indicates interaction of time with we as a humans. Time waits for no one. It is the most neutral entity in our life which is not affected by anything rather everything is under the influences of the time. The poet wants reader to fill a minute with sixty second means being aware of every moment we are going through and doing justice with it, investing it in doing good things.
Yours is the Earth and everything that’s in it,
And—which is more—you’ll be a Man, my son!
Yep, after all of these conditions, all these ifs- one can achieve and enjoy everything that makes his/her life complete.
Stoicism in ‘If-‘
The poem is considered as one of the best depictions of the principles of Stoicism, the ‘Stoic’ philosophy. According to stoicism, a stoic person is one who remains unaffected by the things happening around him/her (It also does not mean that remaining dumb or numb) The Wikipedia definition is “someone who is indifferent to pain, pleasure, grief, or joy”.
Stoicism is based on the idea that all of the things happening around us are made up of cause and effect. Sometimes, we know the cause behind anything but it is practically impossible to know cause behind everything and after knowing that cause – change its effect to our desired results. There will always be something which will not be in our control. This idea of having rational structure of universe made up of cause and effect is called as ‘Logos’ in Stoicism.
The stoicism tries to establish that we cannot always know or remain aware of the logic behind everything happening with us and around us. ‘We’ – a person not being aware of ‘the cause’ of happening this ‘thing’ will not prevent the ‘thing’ from happening. It means that some things will always remain out of our control and our expectations. Hence the best you can do is to establish the control on things which are in immediate influence of you.
Hence,
Rather than expecting the world to be ‘ideal’ to anyone’s expectations – the stoic accepts the world ‘as it is’. In order to grow through this world, a stoic controls that thing which is in his/her immediate control. The poem ‘If-‘ by Rudyard Kipling does the excellent job of describing the virtues if a Stoic and what can be done and controlled to achieve greatness.
There are two pillars of Stoicism: Four cardinal Virtues and the dichotomy of control.
Pillar I- Four cardinal Virtues
Wisdom– the idea good and bad
Temperance– no overdoing and under doing things, doing the optimum, doing what is necessary
Justice– the awareness of what is right for given situation of a person or a society
Courage– the knowledge of justice and to standing for it
Pillar II-The dichotomy of control
This is the most important and the most famous idea in the stoicism. The dichotomy simply separates the things which are in our control and things which are not in our control.
The best way to deal with the things which are not in our control is to accept them as they are and the best thing to deal with the things that are in our control is to act on them immediately so as to eventually shape the reality we expect.
The best thing about the stoicism is that it was developed by people representing different levels of society. “Zeno of Cyprus” known as a father of Stoicism was a wealthy merchant in Athens who turned to the development of stoicism when he had lost all his possession in a shipwreck. With nothing in hand, he turned to a book shop and got influenced by the ideas of Socrates. Epictetus, the person who was a slave also contributed to the stoicism in a great way. Actually, the meaning of Greek word Epictetus (ἐπίκτητος) is “gained” or “acquired”. The real name of this slave is not known to anyone and there are no known writings by Epictetus available. All his knowledge was transcribed by his pupil Arrian and published as “Disclosures” and “Enchiridion“
"Men are disturbed not by the things which happen,
but by the opinions about the things."
- Epictetus, Enchiridion
The same idea Rudyard expresses in the poem when he asks reader to remain sane and confident when peoples are doubting him/her.
Marcus Aurelius who was a Roman Emperor and one of the greatest philosophers was also a stoic. Marcus Aurelius and emperor was influenced by the ideas of Epictetus- a slave. He wrote all his ideas in his famous book called Meditations. Nelson Mandela’s colleagues smuggled this book while he was in jail. This same book influenced Mandela to move away from the idea of revenge and think for the betterment of the society while he was in jail.
“It is not death that a man should fear, but he should fear never beginning to live.”
- Marcus Aurelius, Meditations
Rudyard indicates the same philosophy about just getting consumed by the thoughts of the consequences and not acting on achieving something. Fear of failures is the real death, understanding that there is no such thing as success or failure will immediately lead to action which is in person’s hand.
“If someone is able to show me that what I think or do is not right, I will happily change, for I seek the truth, by which no one was ever truly harmed. It is the person who continues in his self-deception and ignorance who is harmed.”
- Marcus Aurelius, Meditations
Rudyard Kipling discusses the same idea of remaining honest to your words, keeping you r promises for it is the only way to differentiate the right and wrong. If you understand that you were right- you will embrace it and if you understand and accept that you were wrong you will learn from it because seeking truth has never truly harmed anyone.
Seneca, one of the famous and important contributors to stoicism was dramatist and satirist.
“We suffer more often in imagination than in reality”
-Seneca
Kipling has also recommended to come out of indecision by doing the things in our immediate control.
In a whole way, when one understands the real meaning behind the poem, the expectations of poet and the philosophy of Stoicism, this gives a great moments of understanding rather enlightenment about the way of life.
‘If-‘ by Rudyard Kipling possibly one of the most important poem in the history of humanity.
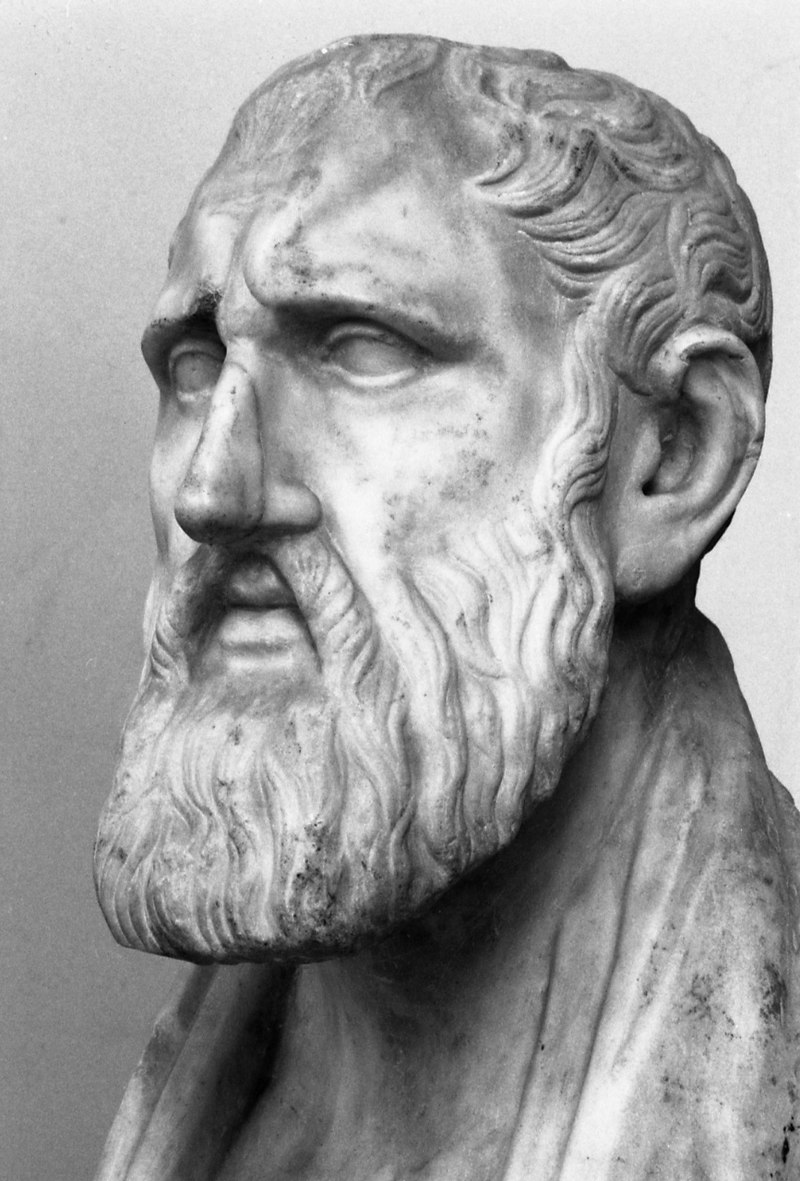
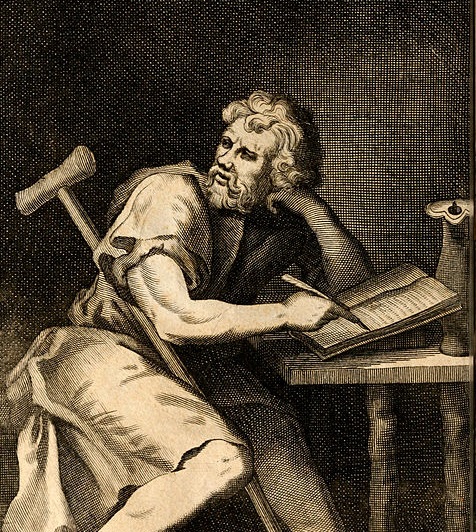
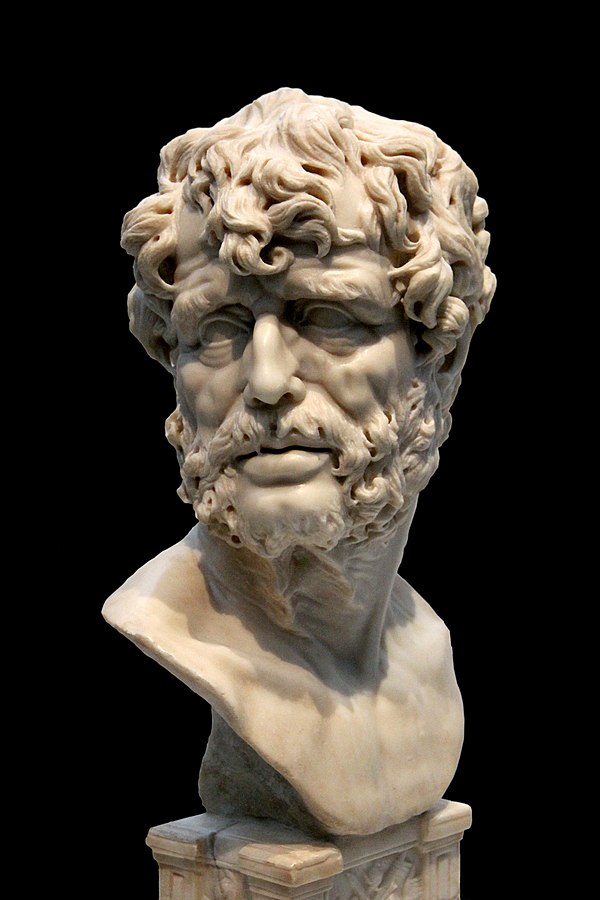
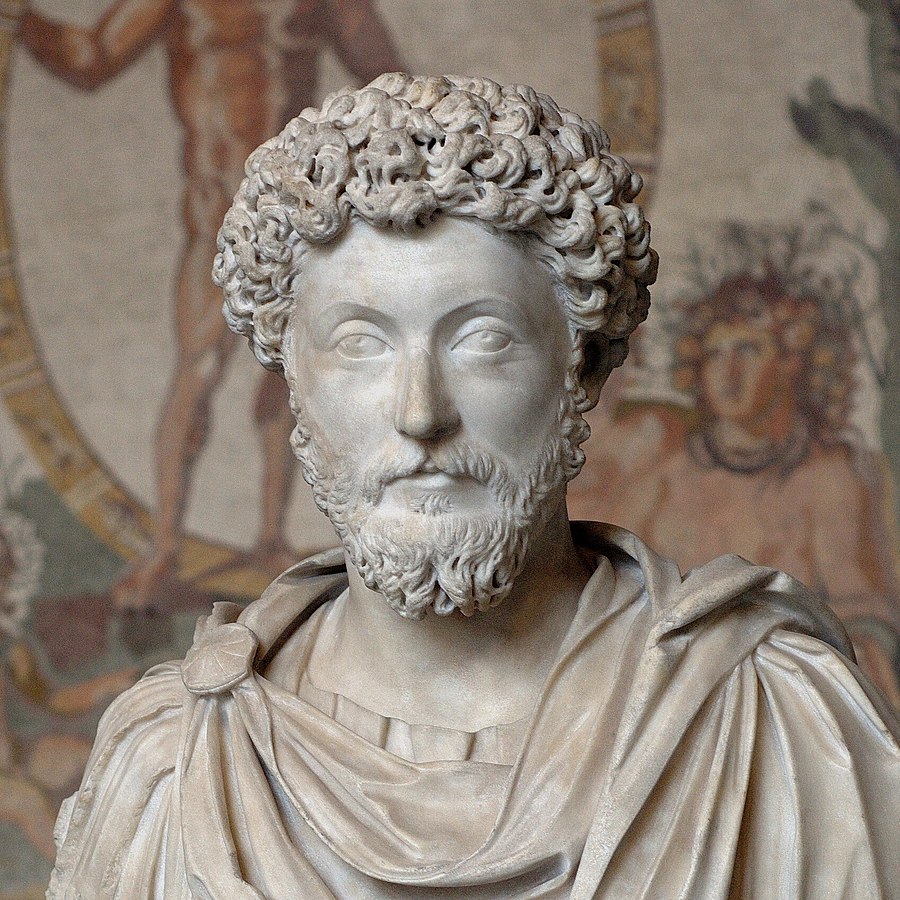




Zeno, Epictetus, Seneca and Marcus Aurelius - The four important Stoics
Image references: